Defining the Format in Data Sources
You can select the format to use in the connector for Azure, Google Cloud, Microsoft OneDrive, S3, and Web Data data sources.
Steps:
1. Select the Data Type:
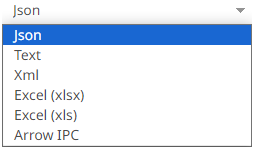
· JSON
If JSON is selected, enter the Record Path which allows the identification of multiple records within the JSON document (e.g., myroot.items.item).
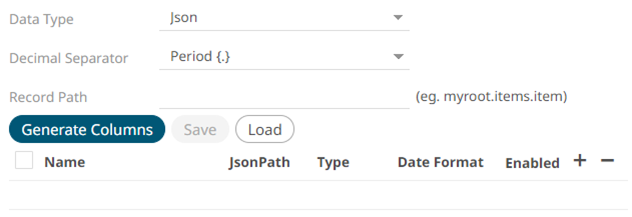
· Text
If Text is selected, confirm the Decimal Separator, Text Qualifier, Column Delimiter, and if the first row of the message includes column headings.
· XML
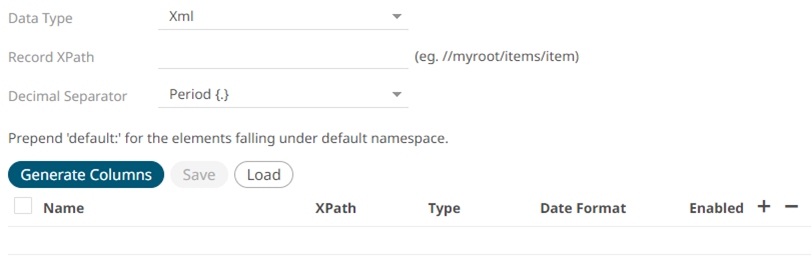
If XML is selected, enter the Record XPath which allows the identification of multiple records within the XML document (e.g., //myroot/items/item).
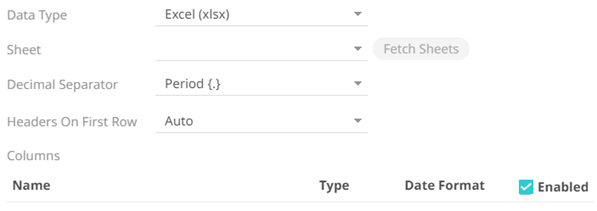
· Excel (xlsx) or Excel (xls)
For Excel file type, select the required sheet and adjust the headers on first row, if needed.
· Arrow IPC
2. Define or set the columns that represent the sections of the file.
|
3. Property |
Description |
|
Name |
The column name of the source schema. |
|
JsonPath/Column Index/XPath |
The JsonPath/Column Index/XPath of the source schema. |
|
Type |
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time |
|
Date Format |
The format when the data type is Time. |
|
Enabled |
Determines whether the message field should be processed. |
|
NOTE |
To parse and format times with higher than millisecond precision, the format string needs to end with a period followed by sequence of uppercase S. There can be no additional characters following them. For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS |
To
delete a column, check its  or all the column
entries, check the topmost
or all the column
entries, check the topmost  , then click
, then click  .
.