Sketch Plane
Select a sketch tool, then select a sketch plane to begin sketching.
A sketch plane can be a global plane, a user-created reference plane, or a planar face of an existing part.
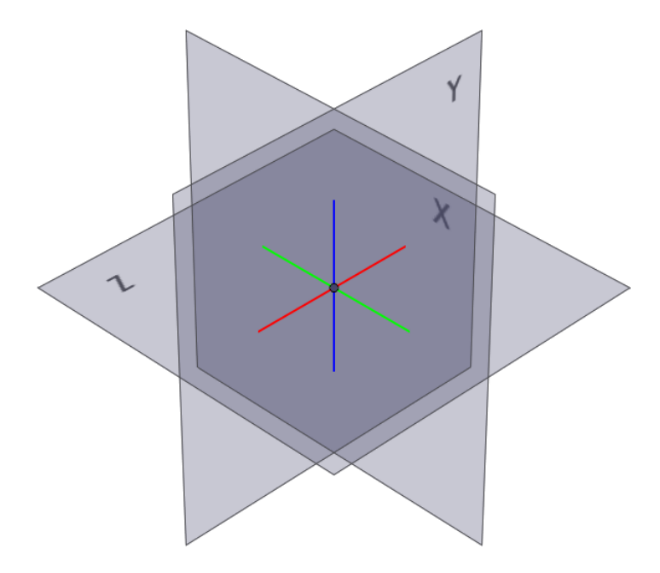 Figure 1. Global Planes
Figure 1. Global Planes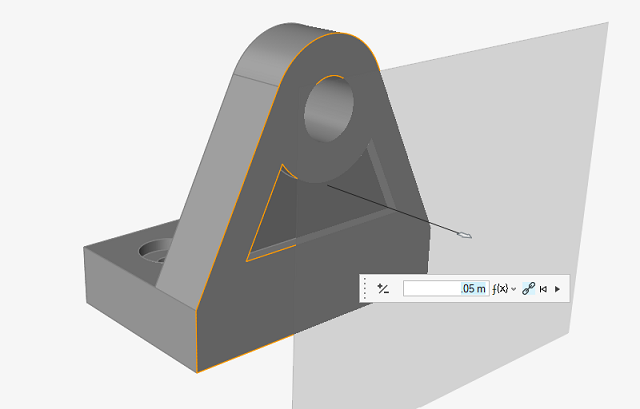 Figure 2. User-Defined Reference Plane
Figure 2. User-Defined Reference Plane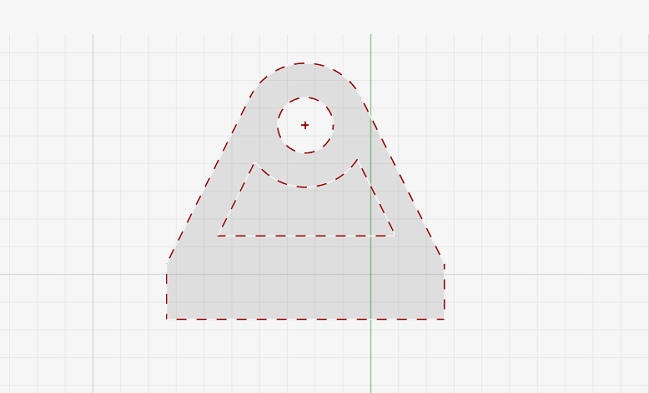 Figure 3. Planar Face on an Existing Part
Figure 3. Planar Face on an Existing Part