Match Topology
Fix gaps between stitched edges and vertices to make the actual geometry of the surfaces consistent with the model topology.
The original geometric entity IDs are also preserved. The same functionality is used for the Optimize for CAD option in the Geometry Export Options dialog.
Example: Match Topology
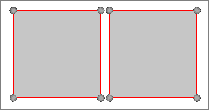
Figure 1. Unrepaired Geometry
 Figure 2. Repaired Geometry not Updated with the Geom Match Topology Tool |
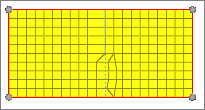 Figure 3. Meshed Geometry |
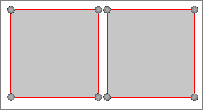 Figure 4. Geometry with Edges Untoggled |
 Figure 5. Repaired Geometry Updated with the Geom Match Topology Tool |
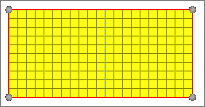 Figure 6. Meshed Geometry |
 Figure 7. Geometry with Edges Untoggled |