Getting Started
Learn how to get started using the Python API.
Launch the Python Console in MotionView
- Launch a new MotionView session and right-click in the Model Browser.
- Click on the Python Window option.
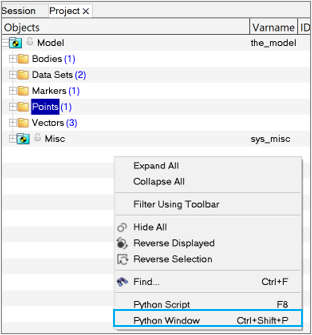
Figure 1.The MV Python Console is launched.
Figure 2.
Python Console Conventions
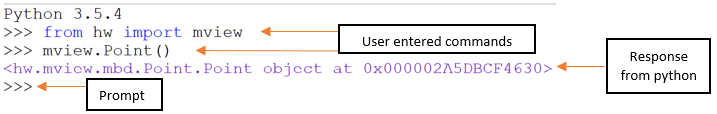
Figure 3.
Importing mview Package
>>> from hw import mviewCreating and Modifying Entities
- Creating Entities
-
>>> from hw import mview# import mview package >>> p1 = mview.Point(name="p_0", x=1, y=4, z=3)# creates a point >>> b1 = mview.Body(name="Body1")# creates a body >>> m1 = mview.Marker(name="Marker1",body=b1,origin=p1)# creates a marker at origin p1 and on body b1 - Accessing Attribute Values
- The dot operator (.) is used to "get" or access class attribute values. You can also
use a getValue function to do the same. These values can be used in
other python expressions. The examples below illustrates this.
>>> p = mview.Point(name="p_0", x=1, y=4, z=-2)# Create a point >>> p.x 1.0# Get x coordinate of a point >>> p.name 'p_0'# Get variable name of the point >>> b = mview.Body(name="b_0", mass=1000, ixx=200, iyy=300, izz=400, cg=p)# Create a body with its cg at location of point p1 >>> b.cg <hw.mview.mbd.Point.Point object at 0x00000162DEB8E940># Get value of the cg, returns the handle of the point it points to >>> b.cg.name 'p_0'# Get the name of this point - Modifying Attribute Values
- In a similar way, you can modify attribute values through dot notation or a
setValue function.
>>> p.y = 2 >>> p.y 2.0# Modify the "y" coordinate value of point "p_0" created previously >>> p.setValue('z', 12) True >>> p.z 12.0# Use setValue function to change "z" coordinate value. Returns True on successfully setting the value >>> b.cg = "P_Global_Origin" >>> b.cg.name 'P_Global_Origin'# Assign the Global Origin to the "cg" of body "b_0" >>> p.setValues(x=11, y=22, z=33) >>> p.x 11.0 >>> p.y 22.0 >>> p.z 33.0# Use setValues function to change multiple values at a time Note: While assigning value to a property which expects an entity reference, for example the cg property of a body, either the full variable name of the entity or the python handle of that entity can be used. - Assign Parametric Values to Attributes
- To assign values which are dependent on properties of other entities, use the full
varname of that property as below.
>>> p1 = mview.Point( name='p_1', x=3, y=3, z=3) >>> p2 = mview.Point( name='p_2', x=2) >>> p2.x = "p_1.x" >>> p2.x 3.0# x coordinate of p2 is expressed in terms of x coordinate of Point p_1 (Parametric expression is given as a string) >>> p1.x = 12 >>> p2.x 12.0# Changing x coordinate of p1 changes x coordinate of p2 - Getting Python Handles of Entities
- To get the python handle to the entity from its variable name use the function
getObjectFromPath().
>>> from hw import mview >>> p = mview.getObjectFromPath("MODEL.System_1.Point_1") >>> p.name 'Point_1' >>> p.parent <hw.mview.mbd.System.System object at 0x00000201C9DF0128># get the handle of a point "Point_1" in "System_1" which is already created You can also get the handle of an entity using the getModel() function which gets the model.>>> p1 = mview.getModel().System_1.Point_1 >>> p1.name 'Point_1'# get the handle of a point "Point_1" in "System_1" which is already created using getModel() function
Saving, Opening, and Exporting Models
>>> from hw import mview
>>> mview.writeFile(r"C:/Temp/example.mdl")
>>> mview.writeFile(r"C:/Temp/example.xml")>>> mview.readFile(r"C:/Temp/example.mdl")>>> mview.runSolverScript(r"C:\Altair\Examples\gearpair1.xml")Python Console Tips and Tricks
- The console can be cleared using the shortcut "Ctrl+L" or %clear.
- Try <Tab> for an auto-complete suggestion for a function or property name.
- Use <F1> for bubble help for an entity/property.
Running Python Scripts
- Right-click in the Model Browser and select Python
Script to browse for a python file containing the script.
OR
- Use the standard python function in the
console.
>>> exec(open(r"C:/Users/username/myscript.py").read())OR
- Use %run command in the
console.
>>> %run C:/Temp/Examples/test.py 1Note: %run is not a standard python command.
Command Logging
- Go to .
- Click on the Enable python window command logging check box.
- Provide a log file to save.