General approach: tube conductor and assimilation conductor
Introduction
This paragraph deals with:
- the general modeling process
- the two modes of description of the conductors in Flux PEEC
(called tube conductor and assimilation conductor )
General process
The general process of modeling in Flux PEEC is presented in the table below. The elements necessary for the description of a conductor and the concepts of tube conductor and assimilation conductor are presented in the following blocks.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Choice of an application (scenario definition) |
| 2 | Conductors description: tube conductor / assimilation conductor |
| 3 | Addition (possibly) of a ground plane |
| 4 | Electric description * |
| 5 | Meshing |
| 6 | Solving process (according to the scenario) |
| 7 | Results post-processing |
* Electric description depends on the choice of the application (Supplied conductors / Conductors impedance)
Description of a conductor …
The description of a conductor includes:
- its geometrical description (topology of the conductor)
- its physical description:
- information related to the material (resistivity and possibly relative permeability)
- information related to the meshing (type of mesh, density)
- the description of its terminals (for electric connections between conductors)
Two modes …
Two types of conductor description are proposed in Flux PEEC, called tube conductor and assimilation conductor. These two modes of description are presented in the two tables below.
| The tube conductor mode enables the description of following conductors | Principal characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| - of rectangular cross-section |  |
|
| - of variously-shaped full cross-section | 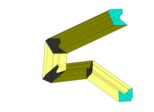 |
|
| - of variously-shaped hollow cross-section with constant layer thickness |  |
|
| The assimilation conductor mode enables the description of following conductors | Principal characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| - of variously-shaped cross-section | ||
| - of full cross-section (rectangular included) | 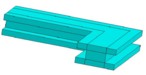 |
|
| - of cross-section characterized by an unspecified number and various shape of holes | 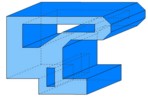 |
|
|
 |
|
These two modes of description are detailed in the following paragraphs.