Finite Element Method (FEM)
The finite element approach is based on the discretization of the domain into a set of finite elements, which are usually triangles or quadrilaterals in a two dimensions and tetrahedral, hexahedra, pyramids or wedges in three dimensions, and using variational principles to solve the problem by minimizing an associated error function or residual.
The unknown variables are approximated over the domain using interpolation procedure in terms of nodal values and set of known functions called shape functions. This approximation is substituted into the governing (conservation) equations in their differential form and the resulting error (residual) is minimized in an average sense using a weighted residual approach.
The variational or weighted residual formulations transforms the governing equations into an integral form called the global weak form. The weak form when applied to each finite element results in a set of discrete equations in terms of the nodal unknown which can then be solved by a number of methods.
- is a differential operator with its associated initial and boundary conditions.
- is the convective flux vector.
- is the diffusive flux vector.
- is the contribution due to a source.
- is the prescribed shape (interpolation) function.
- is the unknown value of the variable at a discrete spatial point .
Finite element method requires transformation of the governing differential equation into an integral equation over the domain. This is accomplished through approaches such as weighted residual formulation and least squares formulation.
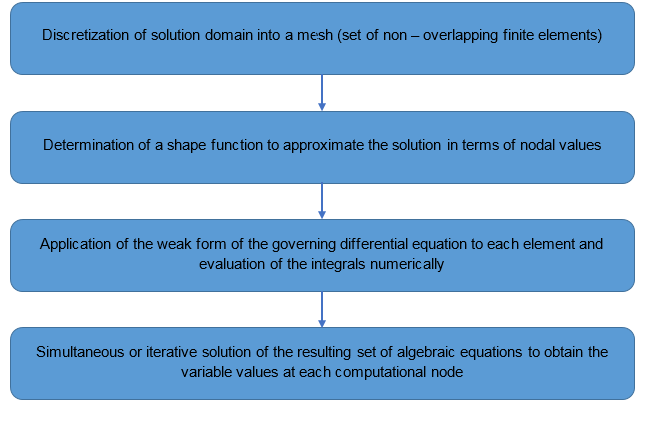
Figure 1. Finite Element Approach
A few of the approaches used to convert the differential equations into their weak integral forms are discussed below.
Weighted Residual Formulation
where , and are the differential operators with lower order derivatives than and represents the domain and the boundary of the domain.
- Point Collocation: where is the Dirac-Delta function. This is analogous to the finite difference approach.
- Subdomain Collocation: for the subdomain (element) and zero elsewhere. This leads to a finite volume formulation.
- Galerkin method: where is a shape function assumed over an element.
- Petrov Galerkin method: . This represents a generalization of all methods except the Galerkin method.
Least Squares Formulation
Galerkin Least Squares Formulation
- represents the Galerkin approximation.
- represents the least squares stabilization.
- represents the inner dot product of the comma separated terms.
- represents the stabilization parameter.