ACU-T: 3100 Conjugate Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 UI Introduction
Problem Description
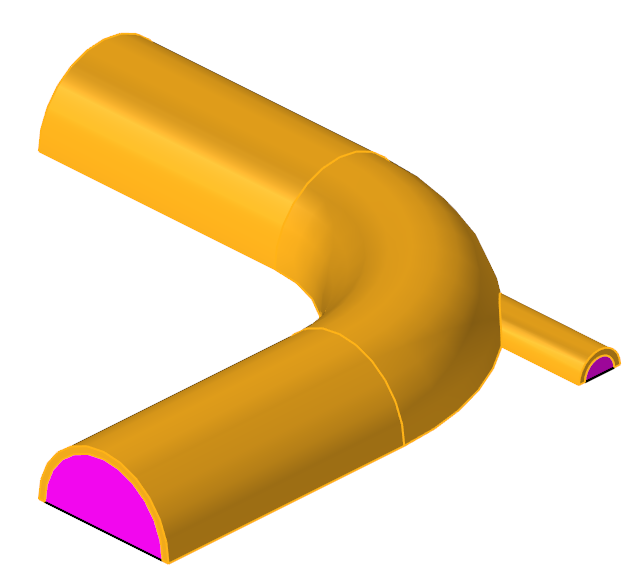
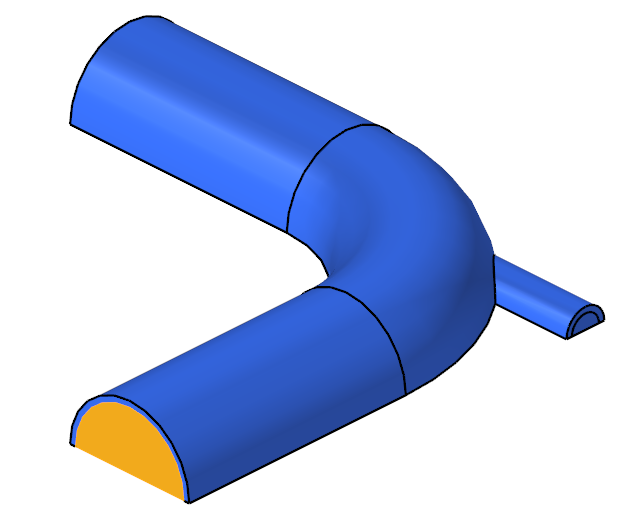
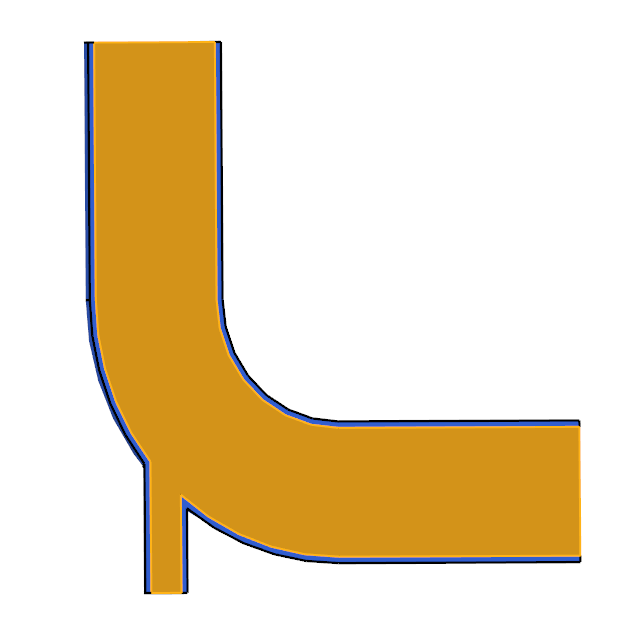
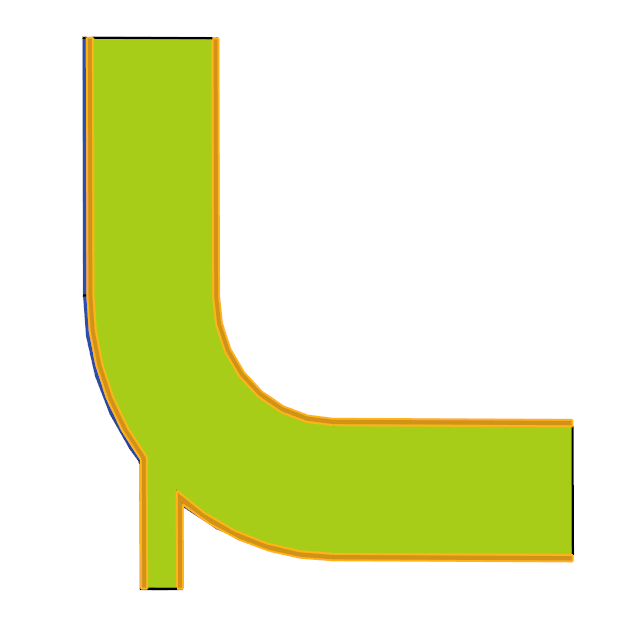
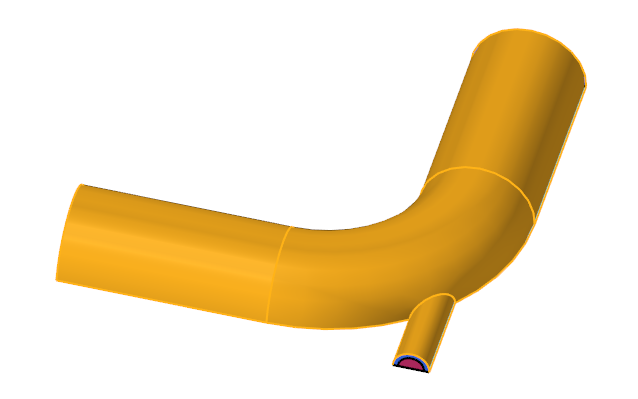
The problem to be addressed in this tutorial is shown schematically in Figure 1. It consists of a mixing elbow made of stainless steel with water entering through two inlets with different velocities and at different temperatures. The geometry is symmetric about the XY midplane of the pipe, as shown in the figure.

Figure 1. Schematic of Mixing Elbow with Stainless-steel Walls
Start HyperMesh CFD and Open the HyperMesh Database
Validate the Geometry
The Validate tool scans through the entire model, performs checks on the surfaces and solids, and flags any defects in the geometry, such as free edges, closed shells, intersections, duplicates, and slivers.

Figure 3.
Set Up the Problem
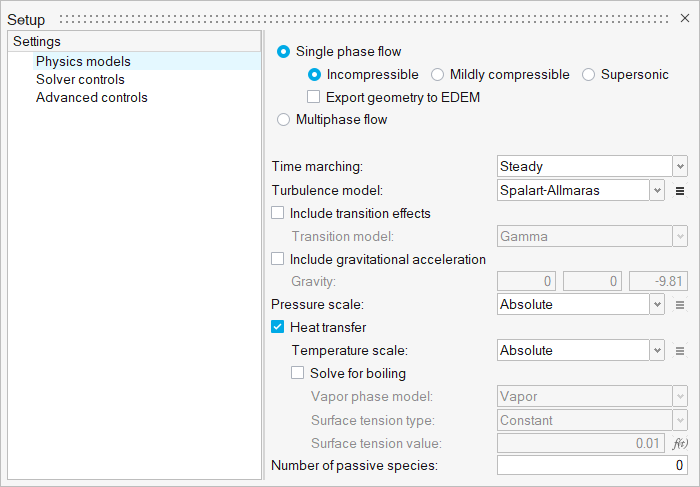
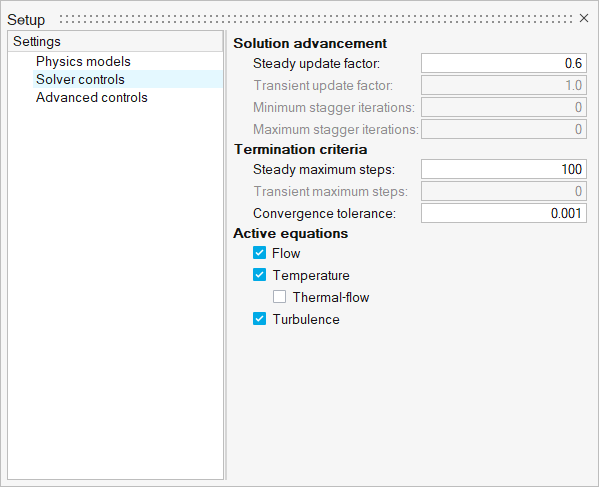
Set Up the Simulation Parameters and Solver Settings
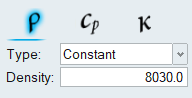
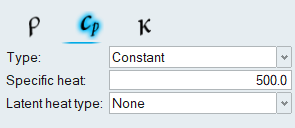
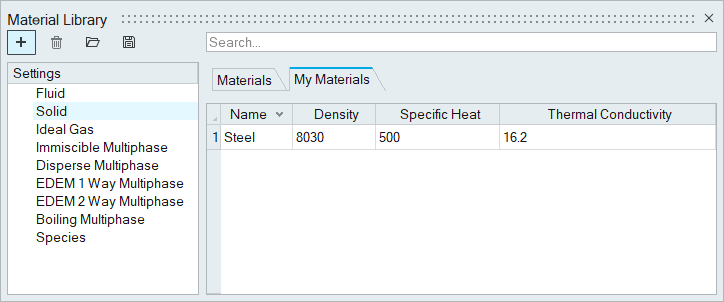
Create a New Material Model
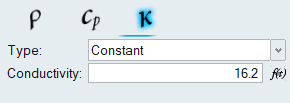
Assign Material Properties
Assign Flow and Thermal Boundary Conditions
Set Boundary Conditions for the Large Inlet
Set Boundary Conditions for the Small Inlet
Set Boundary Conditions for the Outlet
Set Boundary Conditions for the Symmetry Planes
This geometry is symmetric about the XY midplane, and can therefore be modeled with half of the geometry. In order to take advantage of this, the midplane needs to be identified as a symmetry plane. The symmetry boundary condition enforces constraints such that the flow field from one side of the plane is a mirror image of that on the other side.
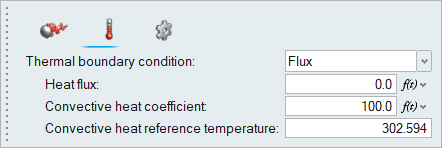
Set Boundary Conditions for the Outer Pipe Walls
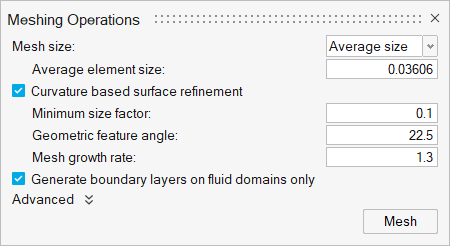
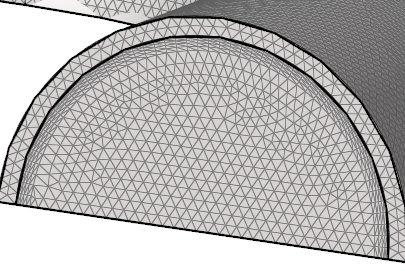
Generate the Mesh
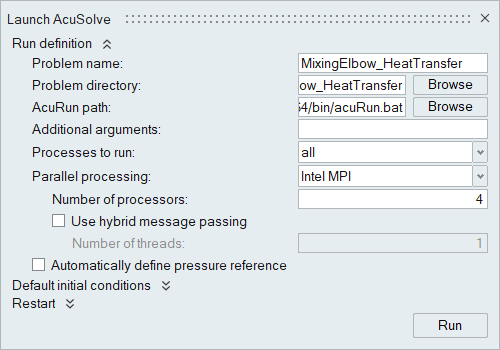
Run AcuSolve
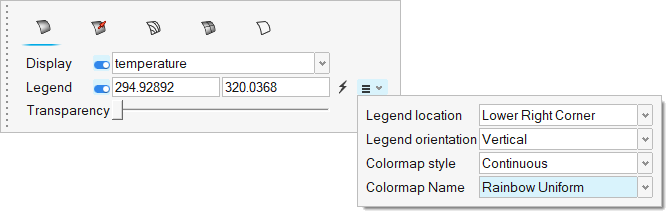
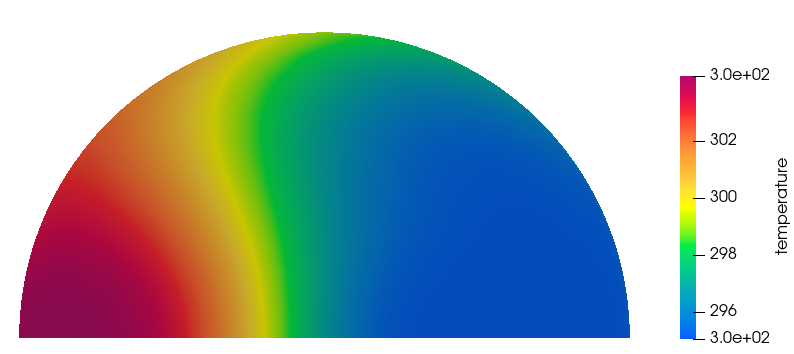
Post-Process the Results with HM-CFD Post
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to set up a conjugate heat transfer simulation using HyperMesh CFD and how to create a new material model. You launched AcuSolve directly from HyperMesh CFD to compute the solution and then post-processed the results using the Post ribbon.