NVIDIA V100 versus NVIDIA Volta RTX 8000
Systems
- DGX 1
- 8x NVIDIA V100 (16 GB, max. 4 GPUs used)
- RTX Server
- 4x NVIDIA Quadro RTX 8000 (48 GB)
- nanoFluidX Software Stack
- nanoFluidX with single precision floating point arithmetic
Results
- Minimal Cube
- Simple cube of static fluid particles at rest
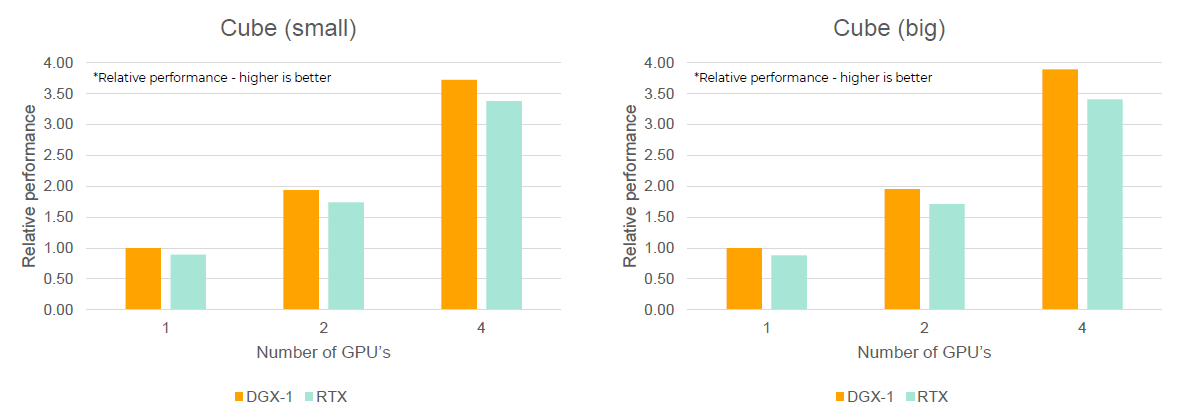
Figure 1.
- Dambreak
- Collapsing water column under gravity in domain (indicated by lines)
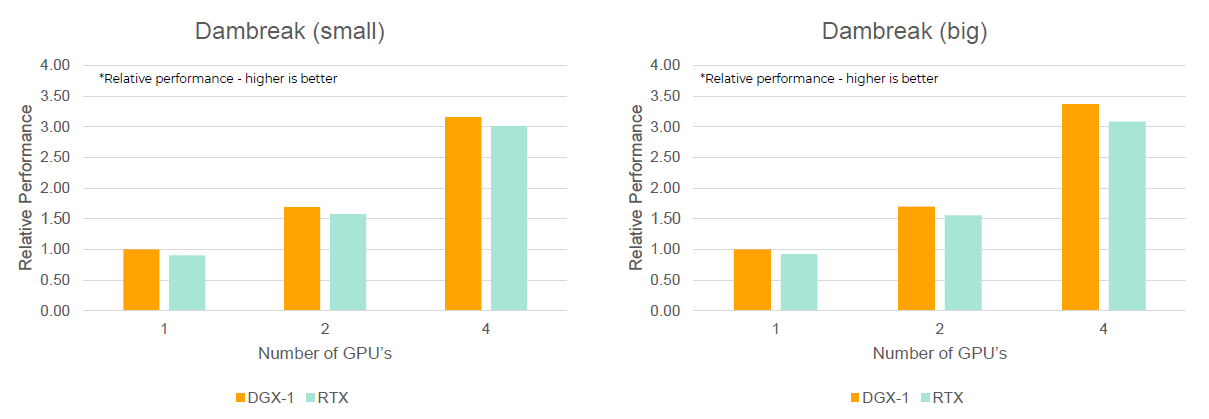
Figure 2.
- Altair E-Gearbox
- Showcase by Altair for E-Mobility application
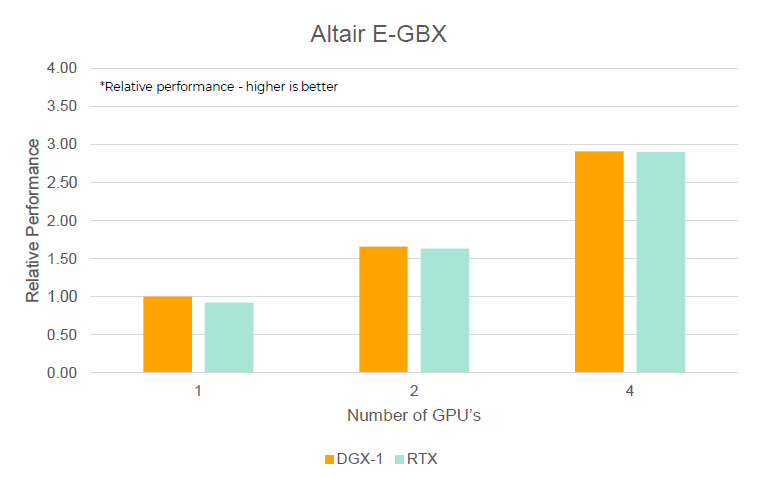
Figure 3.
- Aerospace Gearbox
- Another showcase for aerospace gearbox applications
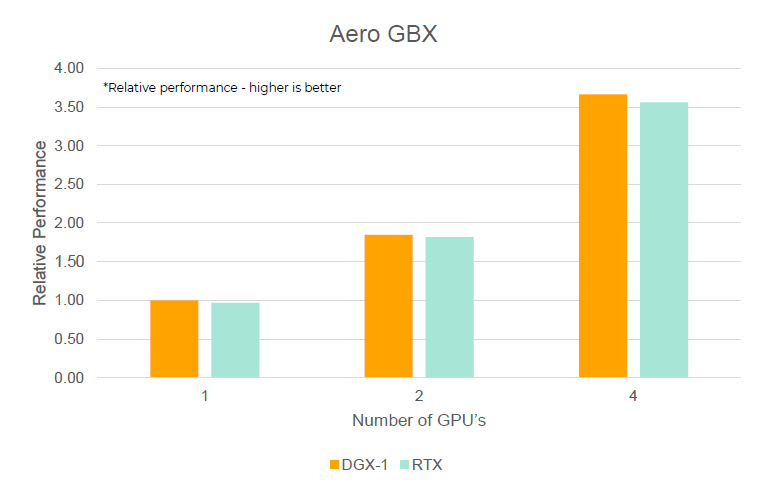
Figure 4.
Conclusions
Results on RTX are generally comparable to DGX-1 with same number of used GPU's. Theoretical performance of the solver core is approximately 10 percent slower on RTX based on Figure 1. This performance difference does not appear in production cases. Generally, performance differences up to 10 percent are not critical as they are not usually noticeable and often depend on minor differences. It is difficult to trace a specific cause because operations and features of the code have different performance characteristics.
Additional Notes
- All cases were run with the WEIGHTED particle interaction scheme.
- All solver output has been deactivated to focus on solver performance, but generally this does not change the results significantly.
- Slight performance uncertainty because of CUDA version as newer versions might apply more tailored optimizations. Compilation for V100 and RTX compute capabilities is not possible in CUDA 8.0.
- Scalability between one and two GPU's is usually slightly impaired because some parts related to multi-GPU may be skipped entirely in single GPU runs.