wagonwheel
This realization creates RBE2 elements for the body, and projects and connects to the hole edge nodes with RBE3 elements.
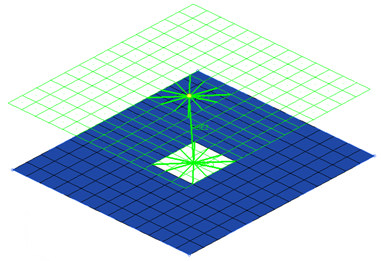
Figure 1.
View new features for Altair HyperWorks 2023.1.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Learn more about the Altair HyperWorks suite of products with interactive tutorials.
Start and configure the applications.
View a list of deprecated panels and their newer, equivalent workflows.
Create, open, import, and save models.
Set up sessions and create report templates.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperMesh.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Browsers provide a structured view of model data, which you can use to review, modify, create, and manage the contents of a model. In addition to visualization, browsers offer features like search, filtering, and sorting, which enhance your ability to navigate and interact with the model data.
Create and edit 2D parametric sketch geometry.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
FE geometry is topology on top of mesh, meaning CAD and mesh exist as a single entity. The purpose of FE geometry is to add vertices, edges, surfaces, and solids on FE models which have no CAD geometry.
Explore the different types of mesh you can create in HyperMesh and create and edit 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D elements.
Create, organize and manage parts and subsystems.
HyperMesh composites modeling.
Create connections between parts of your model.
Use the Connector Browser to view and modify connectors in the current model.
Use the Control Manager to create and edit the various types of controls that will be used later when realizing connectors.
Use the tools in the Create tool set to create connectors, assign controls, and realize.
Create a dummy connector entity to add mass to a part, or create areas of mass to represent parts not present in the CAD or FE data.
Use the Quality controller to perform various checks on connectors and realized FE.
Use the FE Absorb tools to create connectors from existing mesh that meet specific types of realizations.
View details for different types of realizations.
A list of realization types that can be specified for point connectors.
A list of realization types that can be specified for fastener connectors.
Creates a RBODY per part with the center nodes connected to the SPRING2N element.
Creates a body with element type ‘Beam44’ element.
Creates RBE2 elements for the head and CBAR element for the body.
Creates a body with element type ‘Link10’ element.
Creates KINCOUP elements for the head and B31 element for the body.
This realization creates a single RBE2 element for the body.
Creates an RBODY elements and a zero length SPRING2N element.
The bolt (metal clip) creates elements, systems, and configurable body elements that connect a clip location.
Connects two solids through holes, or connects one solid through a hole with a solid blind hole.
Creates CERIG element for the head and LINK10 element for body.
Creates RBE2 (Nastran/OptiStruct) or KINCOUP (Abaqus) elements for the head and body.
Creates CERIG elements for the head and BEAM44 element for the body.
Creates CERIG element for the head and LINK10 for body.
Creates RBE2 (Nastran/OptiStruct) or KINCOUP (Abaqus) elements for the head and CBAR (Nastran/OptiStruct) or B31 (Abaqus) element for the body.
Creates RBE2 (Nastran/OptiStruct) or KINCOUP (Abaqus) elements for the head and body.
Creates RBE2 (Nastran/OptiStruct) or KINCOUP (Abaqus) elements for the head and the body.
Creates CERIG elements for the head and the LINK10 element for body.
Creates RBE2 (Nastran/OptiStruct) or KINCOUP (Abaqus) elements for the head and the body.
Creates a single RBE2 element for the body.
Creates a ConNode rigidlink element for the body.
This realization creates a single ConNode rigidlink element (LS-DYNA) or RBE2 (Radioss) for the body, and projects and connects to nodes of the adjoining shell/solid within the prescribed cylinder diameter, L1 (cylinder height along the vector from the connector location) and L2 (cylinder height in the opposite direction of the vector from the connector location).
Creates KINCOUP elements for the head and B31 element for the body.
Creates a RgdBody rigidlink element for the body.
Creates a RgdBody rigidlink element for the body.
This realization creates RBE2 elements for the body, and projects and connects to the hole edge nodes with RBE3 elements.
A list of realization types that can be specified for line connectors.
A list of realization types that can be specified for area connectors.
Organize elements into connector groups.
The FE configuration file (feconfig.cfg) is used to define custom welds such as ACM (Area Contact Method) and other special types.
Attachments are an entity to facilitate the ease of joining subsystems.
Use the Connector tools to further define connections between components.
Abstract information incoming from the CAD hierarchy to robustly create connectors.
Rapidly change the shape of the FE mesh without severely sacrificing the mesh quality.
Create a reduced ordered model to facilitate optimization at the concept phase.
Workflow to support topology optimization model build and setup.
Setup an Optimization in HyperMesh.
Multi-disciplinary design exploration and optimization tools.
Validate the model built before running solver analysis.
Models require loads and boundary conditions in order to represent the various physics and/or physical equivalents to bench and in-use testing.
Reduce a full 3D model with axisymmetric surfaces while accounting for imperfections.
Tools and workflows that are dedicated to rapidly creating new parts for specific use cases, or amending existing parts. The current capabilities are focused on stiffening parts.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Use airbag folder utilities and export a resulting airbag in a Radioss deck.
Essential utility tools developed using HyperMesh-Tcl.
Import an aeroelastic finite element model with Nastran Bulk Data format.
Framework to plug certification methods to assess margin of safety from the model and result information.
Create and evaluate evaluation lines and optimize interfaces to eliminate squeak and rattle issues.
Use PhysicsAI to build fast predictive models from CAE data. PhysicsAI can be trained on data with any physics or remeshing and without design variables.
Results data can be post-processed using both HyperMesh and HyperView.
HyperGraph is a data analysis and plotting tool with interfaces to many file formats.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multibody Dynamics.
MediaView plays video files, displays static images, tracks objects, and measures distances.
Use TableView to create an Excel-like spreadsheet.
TextView math scripts reference vector data from HyperGraph windows to automate data processing and data summary.
Create, define, and export reports.
Explore, organize and manage your personal data, collaborate in teams, and connect to other data sources, such as corporate PLM systems to access CAD data or publish simulation data.
Create connections between parts of your model.
View details for different types of realizations.
A list of realization types that can be specified for fastener connectors.
This realization creates RBE2 elements for the body, and projects and connects to the hole edge nodes with RBE3 elements.
This realization creates RBE2 elements for the body, and projects and connects to the hole edge nodes with RBE3 elements.

© 2023 Altair Engineering, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Intellectual Property Rights Notice | Technical Support | Cookie Consent