Imprint
Use the Imprint tool to imprint geometry or mesh onto target surface/lines or elements creating new edges/fixed points or a mesh patch respectively.
Imprinting points on lines or surfaces creates geometry vertices similar to using the Split: Interactive tool. Imprinting surfaces onto surfaces imprints all of the source surfaces' edges onto the target surfaces.
 .
.Imprinting elements / FE geometry to elements / FE geometry obeys post
imprint options of FE tab in  .
.
- Split multiple surfaces with multiple lines at once.
- Use the Split: Interactive tool to untrim previously imprinted surfaces.
- Use the Stitch tool to suppress imprinted edges.
CAD Options
- Maximum imprint distance
- Use maximum imprint distance between source and target geometry.
- Maximum distance
- Enter an imprint distance.
- Line extension method
- Select a line extension option.
- Keep line endpoints
- Keep line endpoints when extending lines.
- Surface imprint method
- Select which lines to imprint.
- Do not imprint internal edges
- Skip internal edges and common edges of selected surfaces.
- Do not imprint near existing edges
- Skip edges too close to pre-existing features.
FE Geometry Options
- Maximum imprint distance
- Use maximum imprint distance between source and target geometry.
- Maximum distance
- Enter an imprint distance.
- Post imprint options
-
- None
- Simple method to imprint source on target surface.
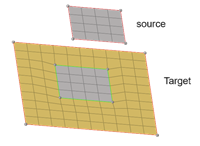
Figure 2. - Create patch between imprinted edges
-
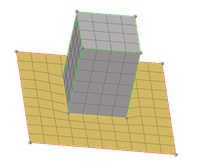
Figure 3. - Move target imprint edges to source
-
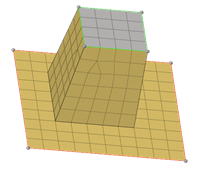
Figure 4. - Move source to target
-
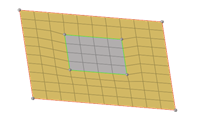
Figure 5.
- Create elements in
- Select to create imprint or patch elements in the following:
- Source component
- Current component
- Destination component
- Do not remesh/rebuild extension
- Use to avoid remesh or rebuild of the patch elements.
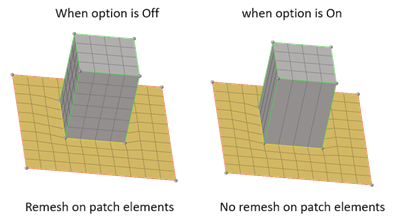
Figure 6. - Closed loop for node list selection
- Use to close the loop of selected node list.
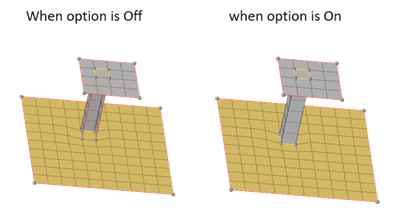
Figure 7. - Do not add fixed points/edges on nodes imprint
- Use to imprint nodes on FE geometry without fixed points or edges.
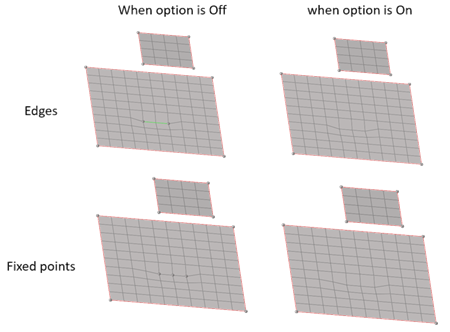
Figure 8.
