This law is a constitutive model for predicting the nonlinear time dependency of
elastomer like materials. It uses a polynomial material model for the hyperelastic material
response and the Bergstrom-Boyce material model to represent the nonlinear viscoelastic time
dependent material response.
This law is only compatible with solid elements.
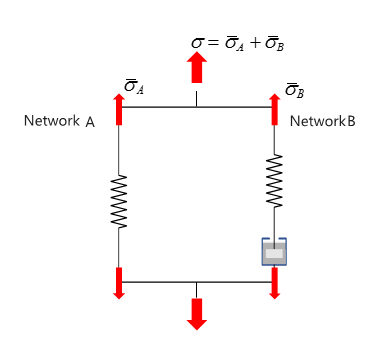
The response of the material can be represented using two parallel networks A and B.
Network A is the equilibrium network with a nonlinear hyperelastic component. In
Network B, a nonlinear hyperelastic component is in series with a nonlinear
viscoelastic flow element, and hence, is time-dependent network.
Figure 1.
Material Parameters
The same polynomial strain energy density formulation is used for the hyperelastic
components in both networks. In Network B, it is scaled by a factor
S
b
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGtbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadkgaaeqaaaaa@384A@
. The strain energy density is then written for the
hyperelastic component of the network.
(1)
W
A
=
∑
i
+
j
=
1
3
C
i
j
(
I
¯
1
−
3
)
i
⋅
(
I
¯
2
−
3
)
j
+
∑
i
=
1
3
1
D
i
(
J
−
1
)
2
i
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGxbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadgeaaeqaaOGaeyypa0ZaaabCaeaacaWGdbWaaSbaaSqa
aiaadMgacaWGQbaabeaakmaabmaabaGabmysayaaraWaaSbaaSqaai
aaigdaaeqaaOGaeyOeI0IaaG4maaGaayjkaiaawMcaamaaCaaaleqa
baGaamyAaaaakiabgwSixpaabmaabaGabmysayaaraWaaSbaaSqaai
aaikdaaeqaaOGaeyOeI0IaaG4maaGaayjkaiaawMcaamaaCaaaleqa
baGaamOAaaaaaeaacaWGPbGaey4kaSIaamOAaiabg2da9iaaigdaae
aacaaIZaaaniabggHiLdGccqGHRaWkdaaeWbqaamaalaaabaGaaGym
aaqaaiaadseadaWgaaWcbaGaamyAaaqabaaaaOWaaeWaaeaacaWGkb
GaeyOeI0IaaGymaaGaayjkaiaawMcaamaaCaaaleqabaGaaGOmaiaa
dMgaaaaabaGaamyAaiabg2da9iaaigdaaeaacaaIZaaaniabggHiLd
aaaa@614A@
and
(2)
W
B
=
S
b
⋅
W
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGxbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadkeaaeqaaOGaeyypa0Jaam4uamaaBaaaleaacaWGIbaa
beaakiabgwSixlaadEfadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqabaaaaa@3F4B@
Where,
I
¯
1
=
λ
¯
1
2
+
λ
¯
2
2
+
λ
¯
3
2
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaaceWGjbGbae
badaWgaaWcbaGaaGymaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcuaH7oaBgaqeamaaDaaa
leaacaaIXaaabaGaaGOmaaaakiabgUcaRiqbeU7aSzaaraWaa0baaS
qaaiaaikdaaeaacaaIYaaaaOGaey4kaSIafq4UdWMbaebadaqhaaWc
baGaaG4maaqaaiaaikdaaaaaaa@4567@
I
¯
2
=
λ
¯
1
−
2
+
λ
¯
2
−
2
+
λ
¯
3
−
2
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaaceWGjbGbae
badaWgaaWcbaGaaGOmaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcuaH7oaBgaqeamaaDaaa
leaacaaIXaaabaGaeyOeI0IaaGOmaaaakiabgUcaRiqbeU7aSzaara
Waa0baaSqaaiaaikdaaeaacqGHsislcaaIYaaaaOGaey4kaSIafq4U
dWMbaebadaqhaaWcbaGaaG4maaqaaiabgkHiTiaaikdaaaaaaa@482F@
λ
¯
i
=
J
−
1
3
λ
i
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGafq4UdWMbae
badaWgaaWcbaGaamyAaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcaWGkbWaaWbaaSqabeaa
cqGHsisldaWcaaqaaiaaigdaaeaacaaIZaaaaaaakiabeU7aSnaaBa
aaleaacaWGPbaabeaaaaa@4036@
C
i
j
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGdbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadMgacaWGQbaabeaaaaa@3930@
and
D
i
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGebWaaS
baaSqaaiaadMgaaeqaaaaa@3842@
Material parameters
The hyperelastic component the Cauchy stress is computed as:
(3)
σ
i
=
λ
i
J
∂ W
∂
λ
i
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaeq4Wdm3aaS
baaSqaaiaadMgaaeqaaOGaeyypa0ZaaSaaaeaacqaH7oaBdaWgaaWc
baGaamyAaaqabaaakeaacaWGkbaaamaalaaabaGaeyOaIyRaam4vaa
qaaiabgkGi2kabeU7aSnaaBaaaleaacaWGPbaabeaaaaaaaa@4421@
The total stress is the summer of stress in network A and network B.
Figure 2.
σ =
σ
¯
A
+
σ
¯
B
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaeq4WdmNaey
ypa0Jafq4WdmNbaebadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqabaGccqGHRaWkcuaH
dpWCgaqeamaaBaaaleaacaWGcbaabeaaaaa@3F47@
Since
W
B
=
S
b
⋅
W
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGxbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadkeaaeqaaOGaeyypa0Jaam4uamaaBaaaleaacaWGIbaa
beaakiabgwSixlaadEfadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqabaaaaa@3F4B@
, then
σ
¯
B
=
S
b
⋅
σ
¯
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGafq4WdmNbae
badaWgaaWcbaGaamOqaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcaWGtbWaaSbaaSqaaiaa
dkgaaeqaaOGaeyyXICTafq4WdmNbaebadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqaba
aaaa@40E1@
and total stress is
σ
=
(
1
+
S
b
)
⋅
σ
¯
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaeq4WdmNaey
ypa0JaaiikaiaaigdacqGHRaWkcaWGtbWaaSbaaSqaaiaadkgaaeqa
aOGaaiykaiabgwSixlqbeo8aZzaaraWaaSbaaSqaaiaadgeaaeqaaa aa@42C2@
.
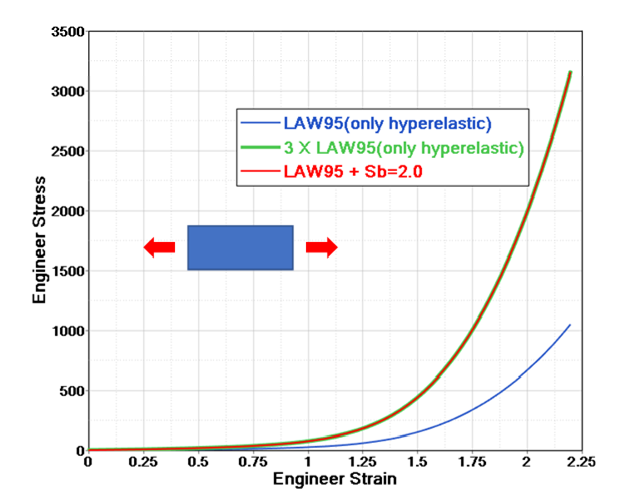
For example, in one tensile test. If use
S
b
=
2
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaam4uamaaBa
aaleaacaWGIbaabeaakiabg2da9iaaikdaaaa@39AE@
, the stress is 3 times of the one without
considering viscous (which means only considered hyperelastic).
Figure 3.
For special values of
C
i
j
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGdbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadMgacaWGQbaabeaaaaa@3930@
, the polynomial model can be reduced to the
following material models.
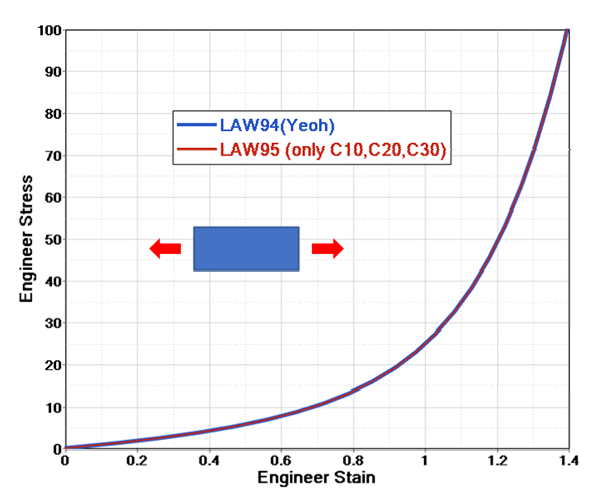
Yeoh:
j
=
0
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamOAaiabg2
da9iaaicdaaaa@38A5@
Where,
C
10
,
C
20
,
C
30
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaam4qamaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaI
YaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaIZaGaaGimaa
qabaaaaa@3EA8@
are not zero.
Figure 4.
Mooney-Rivlin:
i
+
j
=
1
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyAaiabgU
caRiaadQgacqGH9aqpcaaIXaaaaa@3A76@
Where,
C
10
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaam4qamaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaI
YaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaIZaGaaGimaa
qabaaaaa@3EA8@
and
C
01
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaam4qamaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaI
YaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaIZaGaaGimaa
qabaaaaa@3EA8@
are not zero and
D
2
=
D
3
=
0
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiramaaBa
aaleaacaaIYaaabeaakiabg2da9iaadseadaWgaaWcbaGaaG4maaqa
baGccqGH9aqpcaaIWaaaaa@3C33@
.
Neo-Hookean: Only
C
10
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaam4qamaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaI
YaGaaGimaaqabaGccaGGSaGaam4qamaaBaaaleaacaaIZaGaaGimaa
qabaaaaa@3EA8@
and
D
1
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiramaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaaabeaaaaa@37A6@
are not zero.
Where,
C
i
j
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGdbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadMgacaWGQbaabeaaaaa@3930@
and
D
i
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGebWaaS
baaSqaaiaadMgaaeqaaaaa@3842@
Material parameters which can be calculated by completing a curve fit
for quasi-static material test data.
RD-E: 5600 Hyperelastic Material with Curve Input , contains a
curve fit example for Mooney-Rivlin and Yeoh material models.
D
1
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiramaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaaabeaaaaa@37A6@
can be calculated from the bulk modulus or left
blank.
The initial shear modulus and the bulk modulus are computed as:
(4)
μ = 2 (
S
b
+ 1
) (
C
10
+
C
01
)
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacqaH8oqBcq
GH9aqpcaaIYaWaaeWaaeaacaWGtbWaaSbaaSqaaiaadkgaaeqaaOGa
ey4kaSIaaGymaaGaayjkaiaawMcaamaabmaabaGaam4qamaaBaaale
aacaaIXaGaaGimaaqabaGccqGHRaWkcaWGdbWaaSbaaSqaaiaaicda
caaIXaaabeaaaOGaayjkaiaawMcaaaaa@4643@
and
(5)
K =
2
D
1
(
1 +
S
b
)
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGlbGaey
ypa0ZaaSaaaeaacaaIYaaabaGaamiramaaBaaaleaacaaIXaaabeaa
aaGcdaqadaqaaiaaigdacqGHRaWkcaWGtbWaaSbaaSqaaiaadkgaae
qaaaGccaGLOaGaayzkaaaaaa@3FD6@
If the bulk modulus of the material is known,
D
1
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiramaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaaabeaaaaa@37A6@
can be calculated, or if
D
1
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiramaaBa
aaleaacaaIXaaabeaaaaa@37A6@
=0, an incompressible material is assumed.
Viscous (Rate) Effects
The effective creep strain rate in Network B is given by:
(6)
ε
˙
B
v
= A
(
λ
˜
− 1 + ξ
)
C
σ
¯
B
τ
r e f
M
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacuaH1oqzga
GaamaaDaaaleaacaWGcbaabaGaamODaaaakiabg2da9iaadgeadaqa
daqaaiqbeU7aSzaaiaGaeyOeI0IaaGymaiabgUcaRiabe67a4bGaay
jkaiaawMcaamaaCaaaleqabaGaam4qaaaakmaalaaabaGafq4WdmNb
aebadaWgaaWcbaGaamOqaaqabaaakeaacqaHepaDdaWgaaWcbaGaam
OCaiaadwgacaWGMbaabeaaaaGcdaahaaWcbeqaaiaad2eaaaaaaa@4D1A@
Where,
λ
˜
=
I
¯
1
3
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacuaH7oaBga
acaiabg2da9maakaaabaWaaSaaaeaaceWGjbGbaebadaWgaaWcbaGa
aGymaaqabaaakeaacaaIZaaaaaWcbeaaaaa@3BE7@
σ
¯
B
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacuaHdpWCga
qeamaaBaaaleaacaWGcbaabeaaaaa@392D@
Effective stress in Network B.
A
,
ξ
,
M
,
C
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGbbGaai
ilaiaaysW7cqaH+oaEcaGGSaGaaGjbVlaad2eacaGGSaGaaGjbVlaa
doeaaaa@4139@
, and
τ
r
e
f
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacqaHepaDda
WgaaWcbaGaamOCaiaadwgacaWGMbaabeaaaaa@3B1C@
Input material parameters.
The material constants
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyqaaaa@36BC@
,
M
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyqaaaa@36BC@
and
C
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyqaaaa@36BC@
are limited to a specific range of real values as
defined in the Reference Guide . If limited data is available, a trial
and error method 1
ξ
,
M
,
C
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGbbGaai
ilaiaaysW7cqaH+oaEcaGGSaGaaGjbVlaad2eacaGGSaGaaGjbVlaa
doeaaaa@4139@
,
S
b
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbbG8FasPYRqj0=yi0dXdbba9pGe9xq=JbbG8A8frFve9
Fve9Ff0dmeaabaqaciGacaGaaeqabaWaaeaaeaaakeaacaWGtbWaaS
baaSqaaiaadkgaaeqaaaaa@384A@
=1.6; and
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyqaaaa@36BC@
=5. Next, compare model predictions with experimental
data for at least one strain rate and adjust
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamyqaaaa@36BC@
to get a fit for the strain rate data.
1 Bergström,
J. S., and M. C. Boyce. "Constitutive modeling of the large strain time-dependent
behavior of elastomers." Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 46, no. 5
(1998): 931-954