HL-T: 1020 Multiaxial Stress-Life (S-N)
In this tutorial you will:
- Import a model to HyperLife
- Select the SN module and define its required parameters
- Create and assign a material
- Assign load histories for scaling the stresses from FEA subcases
- Evaluate and view results
Import the Model
-
From the Home tools, Files tool group, click the Open Model tool.

Figure 1. -
From the Load model and result dialog, browse and select
HL-1020\Ibeam.h3d for the model
file.
The Load Result field is automatically populated. For this tutorial, the same file is used for both the model and the result.
-
Click Apply.
Figure 2.
Tip: Quickly import the model by dragging and
dropping the .h3d file from
a windows browser into the HyperLife
modeling window.
Define the Fatigue Module
-
Click the SN tool.
The SN tool should be the default fatigue module selected. If it is not, click the arrow next to the fatigue module icon to display a list of available options.

Figure 3.The SN dialog opens. -
Define the SN configuration parameters.
- Select Multi Axial as the method.
- Select MPa for the FE model units.
- Enter a value of 20 for the number of planes.
- Enter a value of 0.5 for the certainty of survival.
- Select GOODMAN for the Tension Damage Model.
- Select NONE for the Shear Damage Model.
- Select Worst for the layer selection.
- Select Time Series for the type of loading.
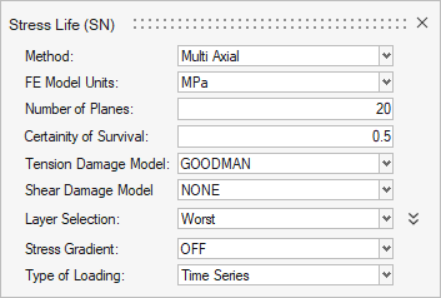
Figure 4. - Exit the dialog.
Assign Materials
-
Click the Material tool.

Figure 5.The Assign Material dialog opens. - Activate the checkboxes next to the parts Flange and Web.
-
Create a new material.
- Click the My Material tab.
-
Click
 to create a new material.
to create a new material.
- Name the material Mat_SN_multiaxial.
- Set the Elastic modulus to 200000.
- Set the Input method to Slope-intcept,2-seg.
-
Accept all other default settings then click Plot &
Save.
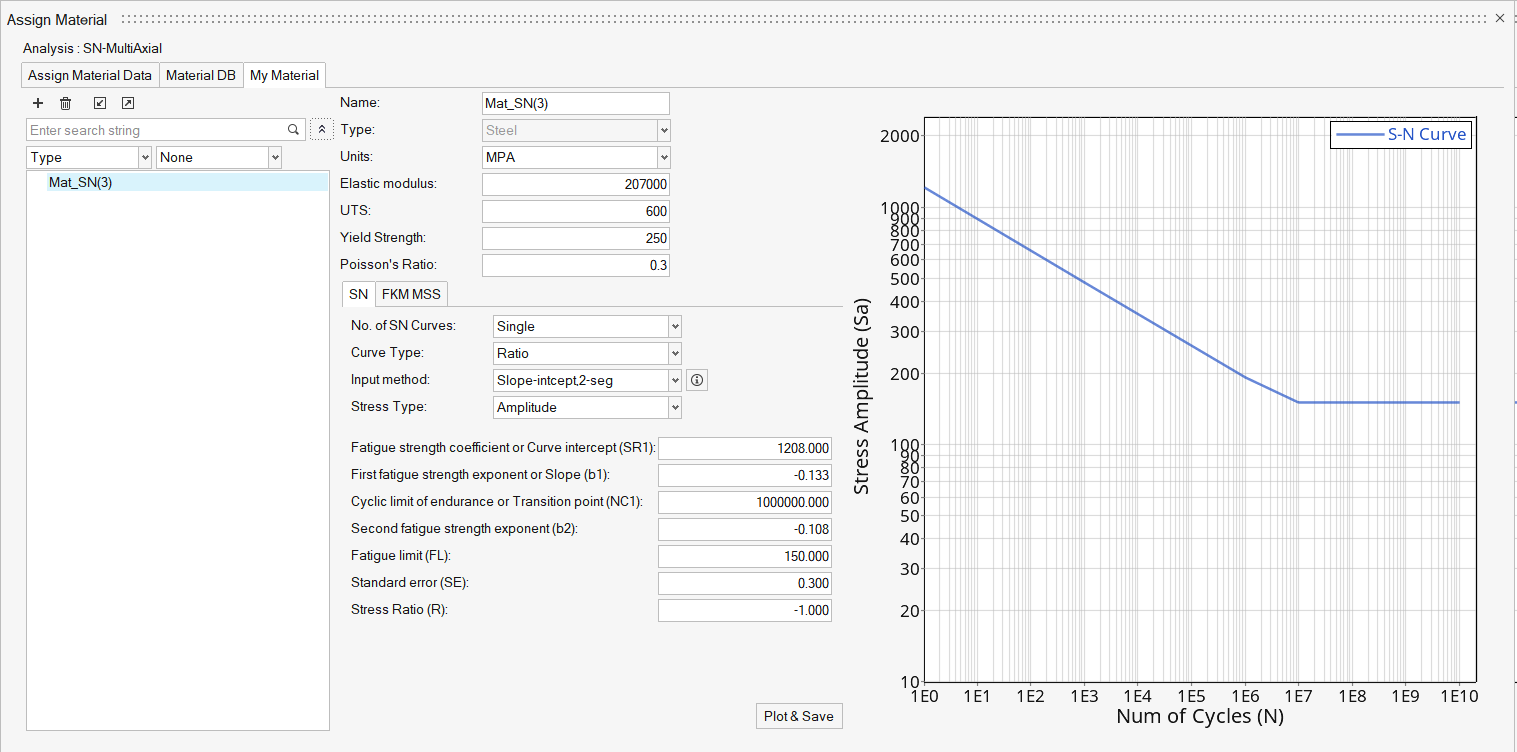
Figure 6.
- Right-click on Mat_SN_multiaxial and select Add to Assign Material List.
-
Return to the Assign Material Data tab and select
Mat_SN_multiaxial from the Material drop-down menu
for both Flange and Web.
The Material list is populated with the materials selected from Material Database and My Material.
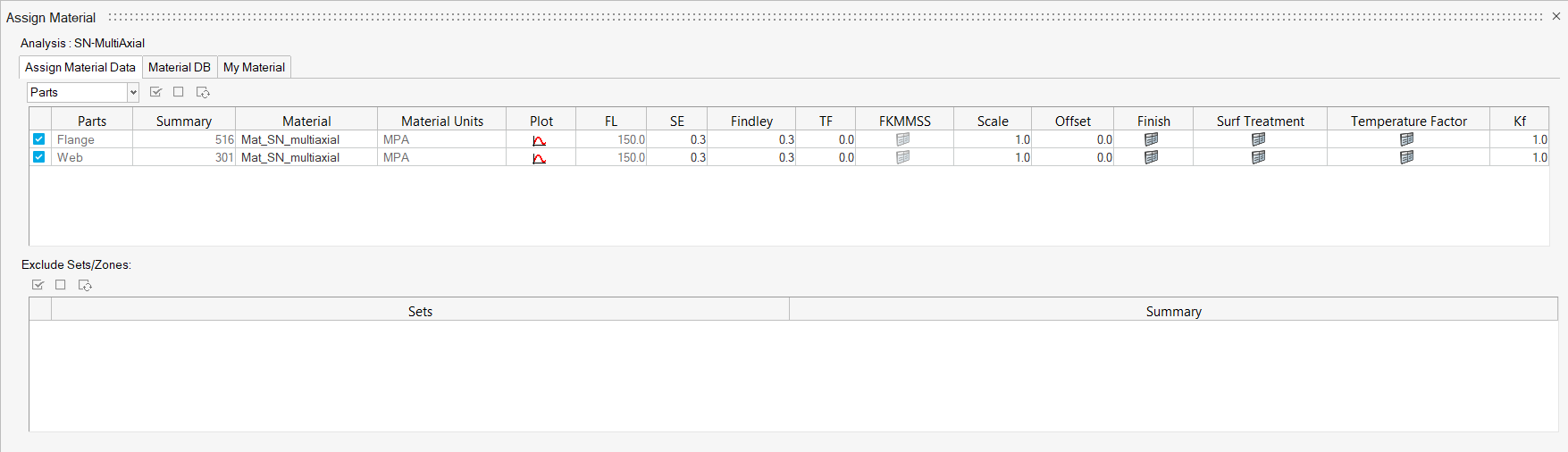
Figure 7. - Exit the dialog.
Assign Load Histories
-
Click the Load Map tool.
Figure 8.The Load Map dialog opens. - From the Channel Type drop-down menu at the top of the dialog, select Time Data.
-
Click
 in the Choose File
field and browse for load1.csv.
in the Choose File
field and browse for load1.csv.
-
Click
 to add the load case.
to add the load case.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for load2.csv, load3.csv, and load4.csv.
- Optional:
Click
 to view a plot of the loads.
to view a plot of the loads.
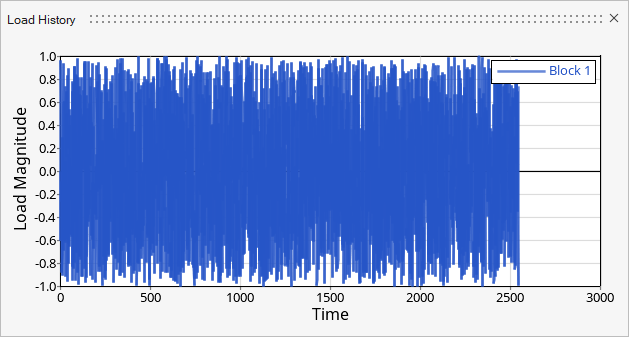
Figure 9. Load 1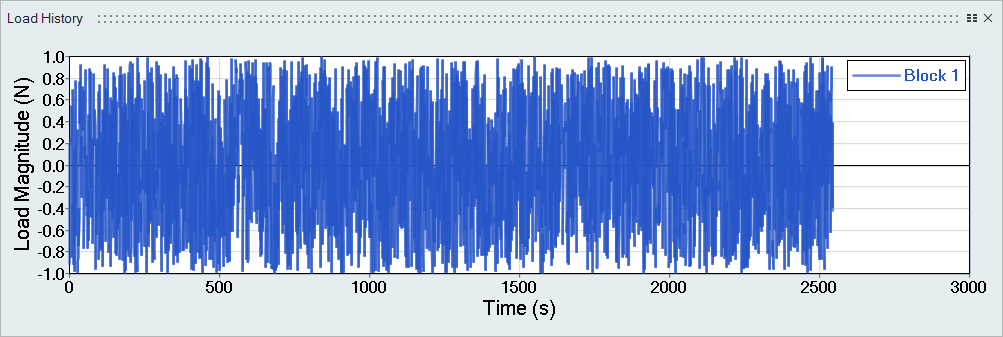
Figure 10. Load 2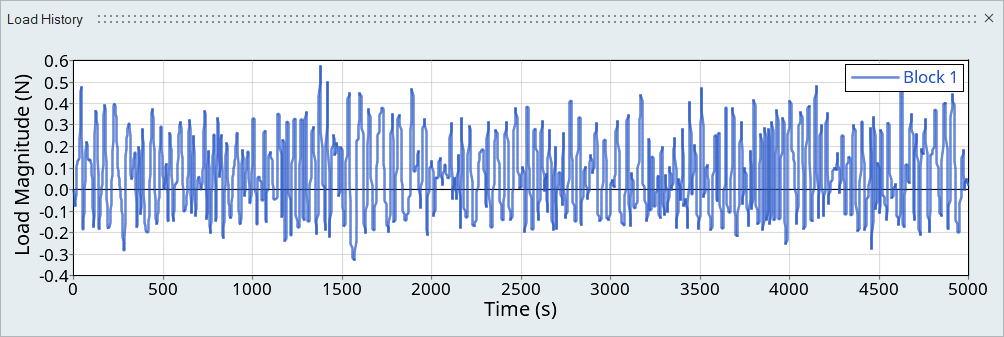
Figure 11. Load 3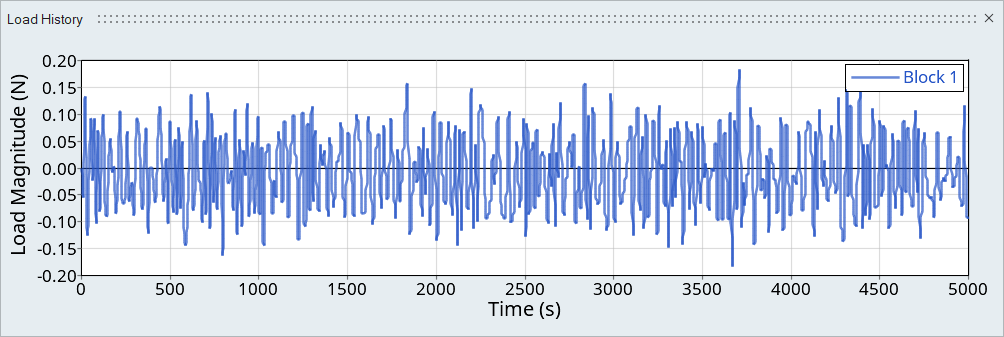
Figure 12. Load 4Tip: Expand the width of the dialog to view a clearer picture of the plot. - On the bottom half of the dialog, set the radio button to Auto for event creation.
-
Select both the load 1 (block1) and load 2
(block1) channels and Subcase 1 and
Subcase 2, then click
 to create the first event.
to create the first event.
- In a similar manner, create a second event by selecting load 3 (block1), and load 4 (block1), Subcase 1, and Subcase 2.
- Activate the checkboxes for the two events.
-
Set the Scale as shown in the image below.
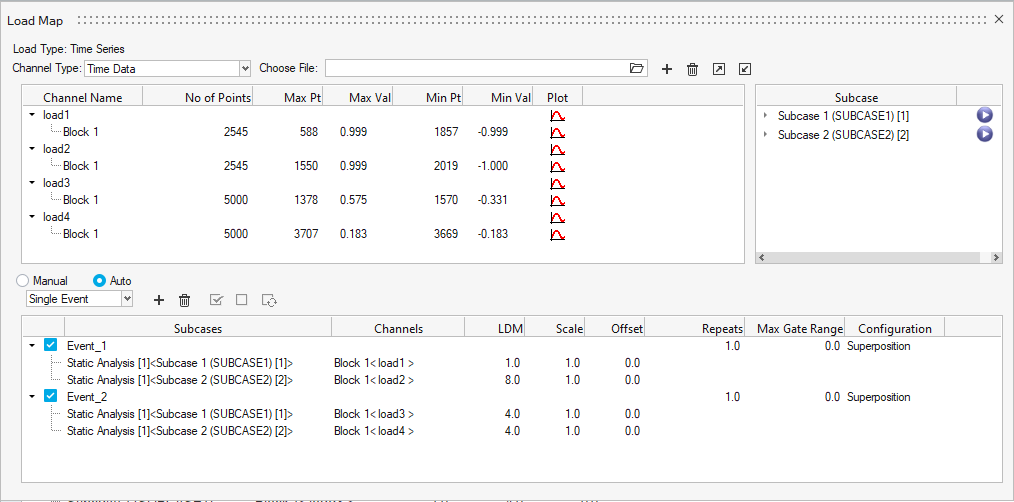
Figure 13. - Exit the dialog.
Evaluate and View Results
-
From the Evaluate tool group, click the
Run Analysis tool.

Figure 14.The Evaluate dialog opens.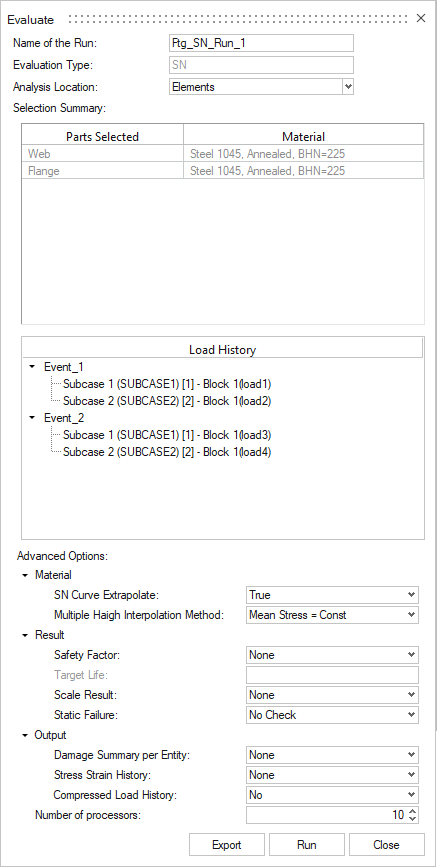
Figure 15. - Optional: Enter a name for the run.
-
Click Run.
Result files are saved to the home directory and the Run Status dialog opens.
- Once the run is complete, click View Current Results.
-
Use the Results Explorer to
visualize various types of results.
The contour below highlights the total damage (Event 1 + Event 2).
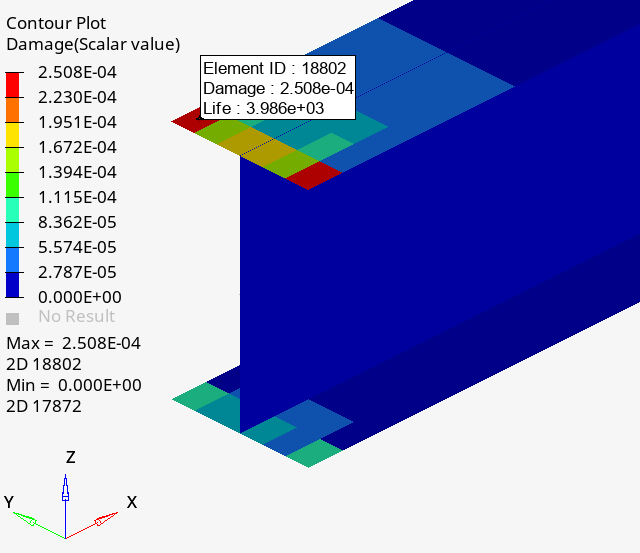
Figure 16.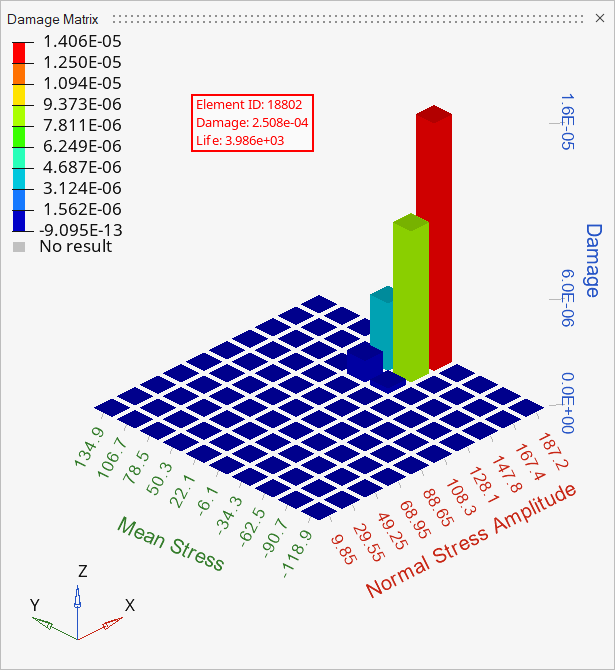
Figure 17. Event 1: Damage matrix for element 18802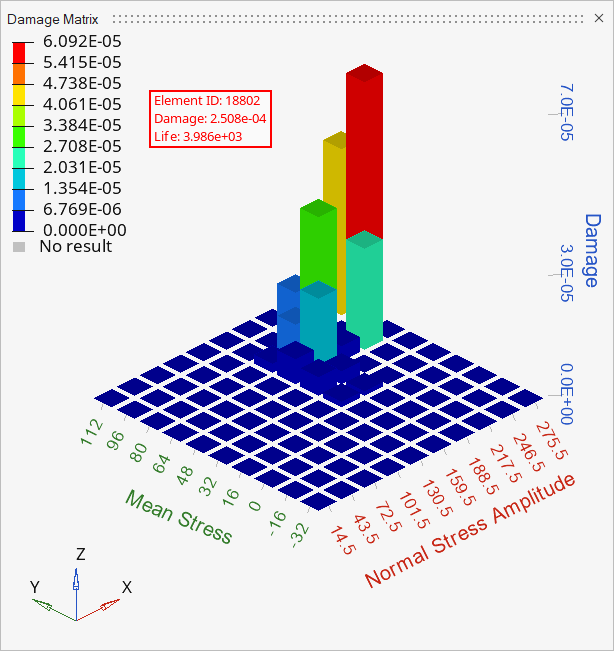
Figure 18. Event 2: Damage matrix for element 18802