<simulation>
The <simulation> category specifies the main parameters of the simulation like the number of iterations, and the file containing the surface mesh or the fluid material.
<simulation> - <general>
- <num_coarsest_iterations>
- Defines the number of iterations at the coarsest refinement level. The physical time per coarsest iteration depends on the material parameters and the Mach factor.
- <mach_factor>
- Specifies the scaling factor for the Mach number (1.0 = Mach-matched
simulation). The time step increases linearly with this factor. With a
value of 2.0, for example, the simulation runs approximately twice as
fast for the same simulated physical time.Note: ultraFluidX is using a weak compressible LBM formulation, which is only valid up to approximately Ma = 0.4, so consider the maximum velocity that may occur in your simulation when setting this parameter to not exceed this limit.
- <moving_ground>
- The wind tunnel ground is a no-slip wall with zero velocity by default. If it should be moving with <reference_velocity> instead, the parameter must be set to true. If belts are specified (<boundary_conditions>), only the belts will move, not the whole ground.
- <rotating_wheels>
- By specifying this parameter, all rotating boundary conditions (<boundary_conditions>) can be switched on or off at once. If set to false, all entries in the <rotating> category will be effectively ignored.
- <boundary_layer_suction>
- Specifies if a part of the wind tunnel ground starting from the inlet to <boundary_layer_suction_xpos> should be treated as a slip wall, instead of a no-slip wall.
- <boundary_layer_suction_xpos>
- Specifies the x-coordinate (in ), where the slip wall will end, if <boundary_layer_suction> is set to true.
- <reference_velocity>
- The reference velocity (specified in ) is used as velocity at the inlet. It is also used as wall velocity for any belts (if specified) or for the whole wind tunnel ground and for the calculation of the aerodynamic coefficients.
<simulation> - <geometry>
- - uFX_domain_x_min
- - uFX_domain_x_max
- - uFX_domain_y_min
- - uFX_domain_y_max
- - uFX_domain_z_min
- - uFX_domain_z_max
- <source_file> or <source_files> - <name>
- Specifies the path to the source file(s) that contain(s) the tessellated surface mesh. The source file(s) must be in ASCII STL format and all surface normals must point outwards, that is, from solid to fluid. ultraFluidX assumes that the STL file is specified in and all other coordinates for bounding boxes, probe locations, etc. are based on the coordinate system of the STL.
- <baffle_parts>
- (Optional) Specifies all parts which are fully two-dimensional, each
part with this property must be identified via the child parameter
<name>. This property should be set for
parts which do not form a closed volume together with other parts and
which are expected to be connected to fluid regions on both sides.
ultraFluidX will then internally create
a duplicate of each of the parts with the appendix “_inv” and inverted
triangle normals to be able to assign proper pressure and wall shear
stress values to both sides of the part. CAUTION:Only specify this property for the baffle part; otherwise, unwanted side effects might occur.
- <surface_mesh_optimization> - <triangle_splitting>
- Specifies the triangle splitting to increase the accuracy of the
calculation of aerodynamics forces that act on the surfaces. Either
global or local splitting can be selected. The default setting is
global, controlled by the following child parameters:
- <active>
- (Global) Switch that activates the triangle splitting.
- <max_relative_edge_length>
- This factor multiplies the voxel size connected to the geometric part to compute the splitting threshold. Setting this factor to zero makes the variable inactive. Negative values are corrected to zero. If this parameter and <max_absolute_edge_length> are both greater than zero, the smaller value per part has precedence.
- <max_absolute_edge_length>
- Absolute threshold (in [m]) of splitting. Default values is set to zero and hence inactive. Negative values are corrected to zero. If this parameter and <max_relative_edge_length> are both greater than zero, the smaller value per part has precedence.
- <triangle_plinth>
- ultraFluidX automatically creates a plinth in regions where single voxels would be squeezed between the wind tunnel ground and, for example, the tire of a car by treating such single voxels as solid. If <triangle_plinth> is set to true, the corresponding surface triangles of these solid voxels will be created to properly visualize the behavior and to increase the accuracy of the calculation of aerodynamic forces in that region.
- <domain_bounding_box>
- The bounding box of the simulation domain, must be specified via the child parameters <x_min>, <x_max>, <y_min>, <y_max>, <z_min> and <z_max> in .
<simulation> - <material>
- <density>
- Density of the material .
- <dynamic_viscosity>
- Dynamic viscosity of the material .
- <temperature>
- Temperature (T) of the material .
- <specific_gas_constant>
- Specific gas constant (R) of the material .
<simulation> - <wall_modeling>
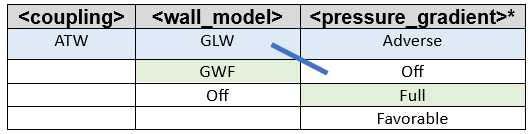
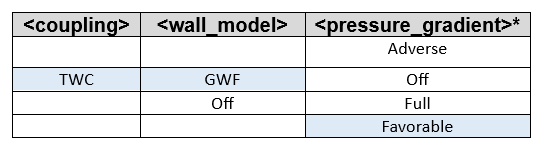
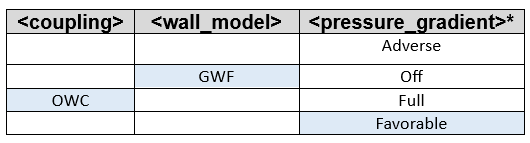
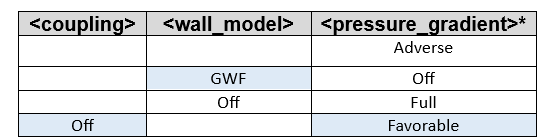
- <coupling> (adaptive_two-way, two-way,one-way, off)
- This parameter exposes coupling options of how to impose wall shear
stress with the velocity at a donor node, given by the LES computation.
Further past the region, the IBB wall boundary condition is updated with
a slip velocity that enforces the target wall shear stress. This wall
shear stress is calculated by supposing that the donor velocity away
from the wall verifies a given theoretical law of the wall, for example,
like the classical log law; see the <wall_model>
parameter below. Different choices for this coupling are available in
ultraFluidX:
- adaptive_two-way
- The adaptive two way wall-LES coupling model imposes the right near wall slope of velocity as well as the right wall eddy viscosity based on the different information collected in the wall vicinity and the chosen law of the wall. This is the latest coupling model. If adaptive_two-way is specified, the bounding walls (excluding inlet and outlet) are automatically defined as link-based (link_based_bc).
- two-way
- The wall shear stress determined using the wall model is used as an input value for the computation of the slip velocity at the wall.
- one-way
- The slip velocity at the wall is not derived via the wall shear stress. It is based on information at the donor position and coming from the LES in the bulk flow and is directly proportional to this value (non-homogeneous Dirichlet for the velocity). The wall shear stress determined by this coupling approach is computed a posteriori, for instance to be used for the estimation of the viscous force contribution.
- off
- No wall model is used with this parameter. It falls back to the classical no-slip boundary condition (homogeneous Dirichlet for the velocity). The wall shear stress determined by this coupling approach is computed a posteriori, only to be used for the estimation of the viscous force contribution.
- <wall_model> (GLW, GWF, WangMoin, off)
- This parameter specifies which theoretical law of the wall should be
used in conjunction with adaptive_two-way or two-way coupling methods in
order to perform an actual Wall Modeled Large Eddy Simulation (WMLES).
Available options:
- GLW (Default for adaptive_two-way coupling method)
- The generalized law of the wall is a continuous function of + and of the streamwise pressure gradient (adverse only, <pressure_gradient> is automatically set to adverse; the only other option is off.) It has the correct trend for small +; a fine enough mesh is necessary to capture this region correctly. More details are given in reference [1] and [2] .
- GWF (Default for two-way coupling method)
- The Generalized wall function is a set of two piecewise-defined functions, one depending on + and the other depending on c where the velocity scale is a mix of the friction velocity and a velocity scale based on the full pressure gradient (<pressure_gradient> is automatically set to adverse; favorable, adverse and off are the alternative options.) More details are given in reference [3].
- WangMoin
- The law of the wall function is not given explicitly but rather a simplified turbulent boundary layer equation (TBLE) where a given pressure gradient is solved for. More details are given in reference [4] and [5].
- off
- The acceptable combinations when using the various coupling methods are shown below. The shaded blue boxes indicate default combinations. The line indicates the allowed combination.
- <pressure_gradient> (favorable, adverse, full, off)
- It is possible to specify the way in which pressure gradients along the
wall should be considered by the wall model.
- off
- The wall model will not consider pressure gradients present in the mean flow field and determine the wall shear stress neglecting the respective pressure-gradient term.
- favorable and adverse
- Consider negative and positive pressure gradients in direction of the flow, respectively.
- full
- Takes any pressure gradient near the wall into account.
<simulation> - <wall_model_variant>
You can specify different wall model settings apart from the global default (specified via <simulation> - <wall_modeling>) on different parts of the vehicle.
- <name>
- Name of the instance, so that it can be referenced in the respective <rotating_instance> or <static_instance> to which it should be applied (mandatory).
- <wall_model> (GLW, GWF, WangMoin, off)
- See above in <simulation> - <wall_modeling>.
- <coupling> (adaptive_two-way, two-way, one-way, off)
- See above in <simulation> - <wall_modeling>.
- <pressure_gradient> (favorable, adverse, full, off)
- See above in <simulation> - <wall_modeling>.