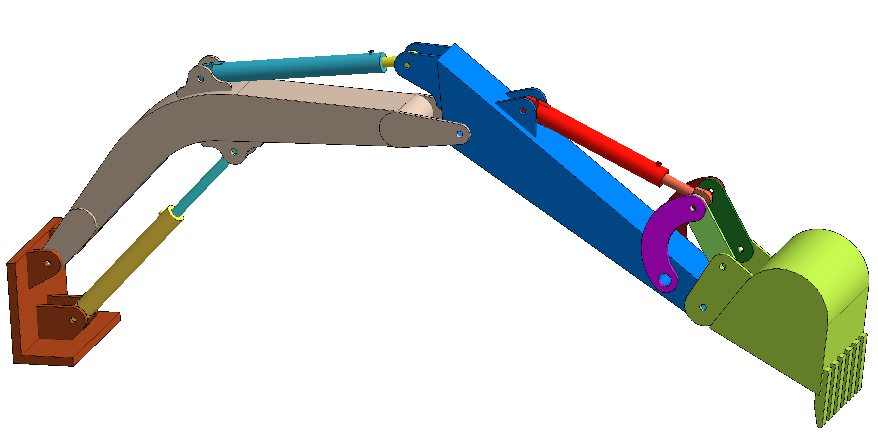
SS-T: 2040 Joints
Create joints in SimSolid.
- Purpose
- SimSolid performs meshless structural
analysis that works on full featured parts and assemblies, is tolerant of
geometric imperfections, and runs in seconds to minutes. In this tutorial,
you will do the following:
- Learn how to create joints - hinge and virtual pins.
- Model Description
- The following model file is needed for this tutorial:
- Joints.ssp
Open Project
- Start a new SimSolid session.
-
On the main window toolbar, click Open Project
 .
.
- In the Open project file dialog, choose Joints.ssp
- Click OK.
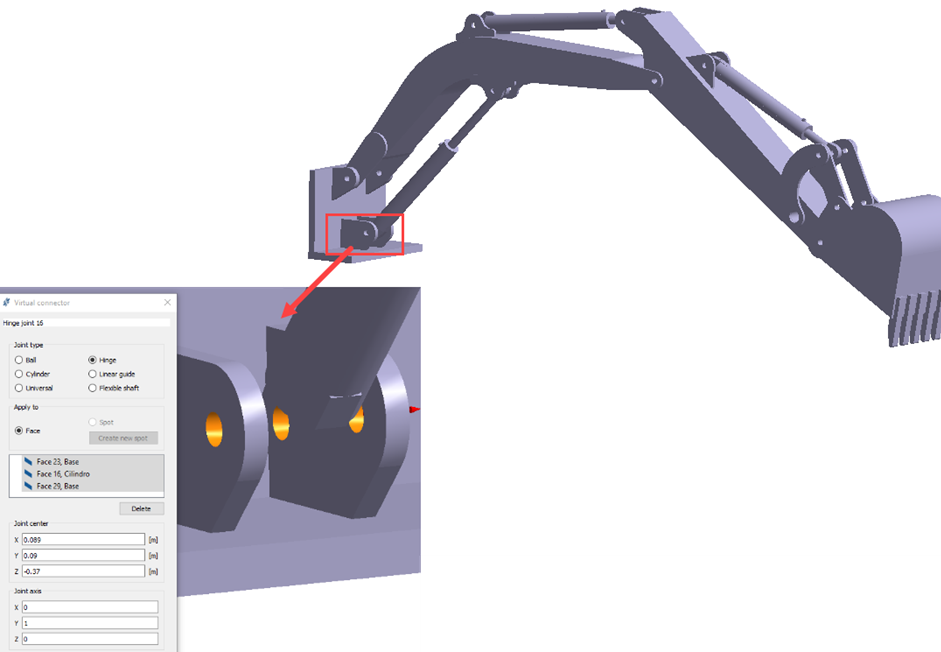
Create Hinge Joints
Create Sliding Contact
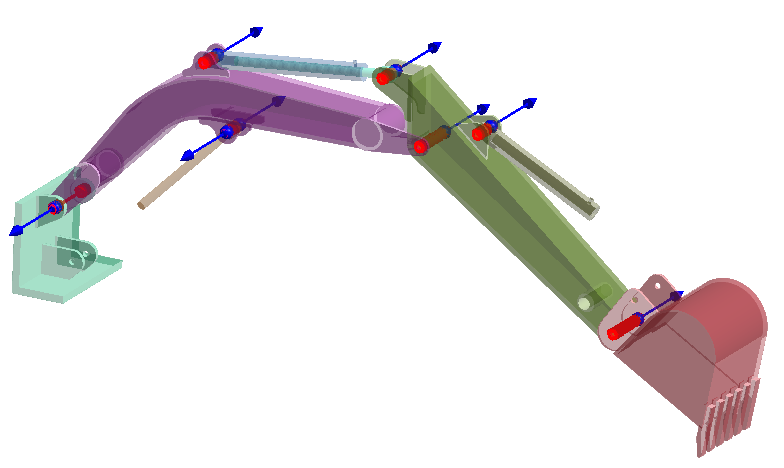
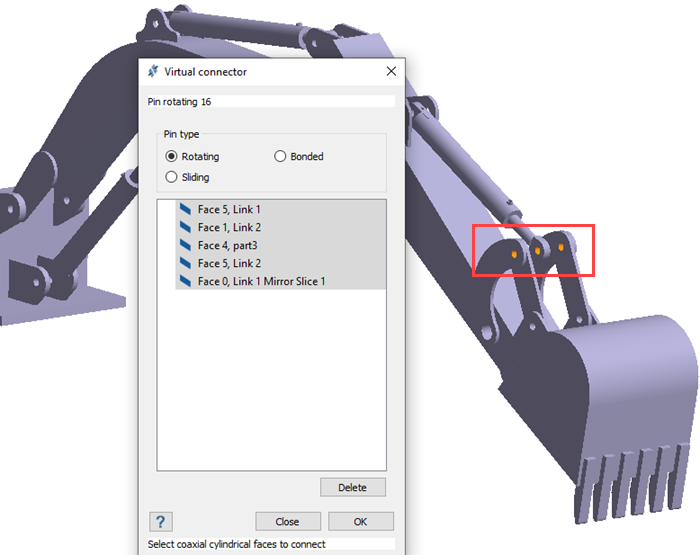
Create Virtual Pin
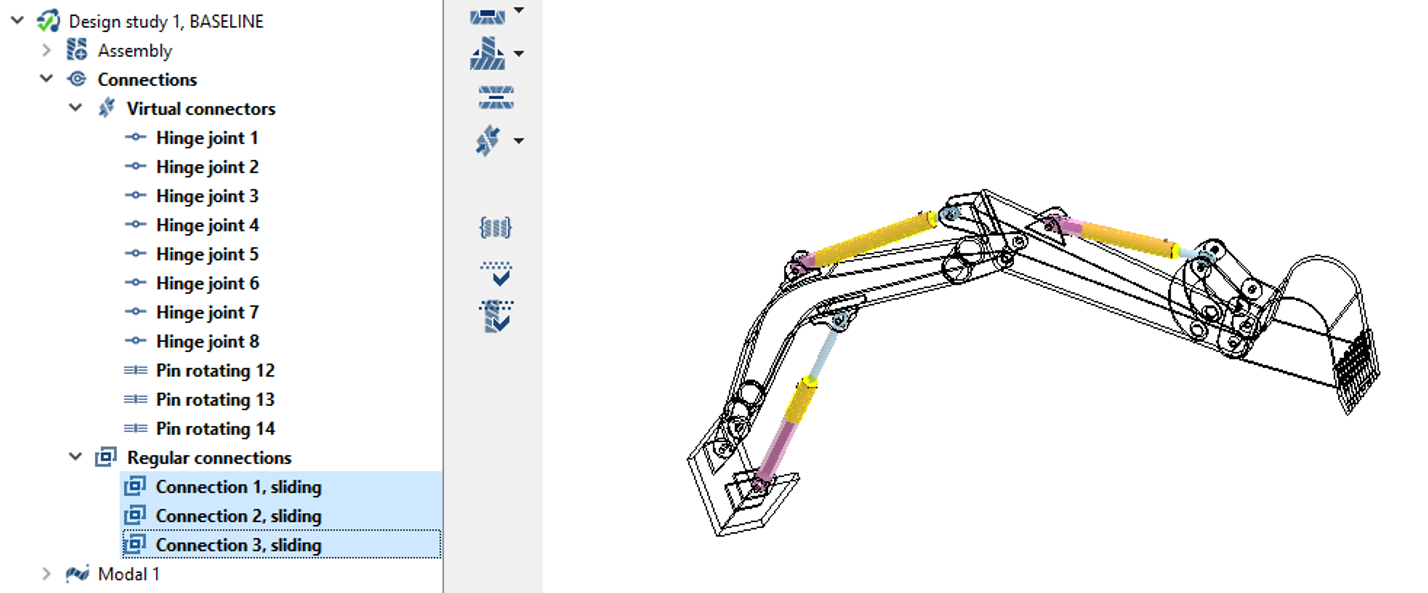
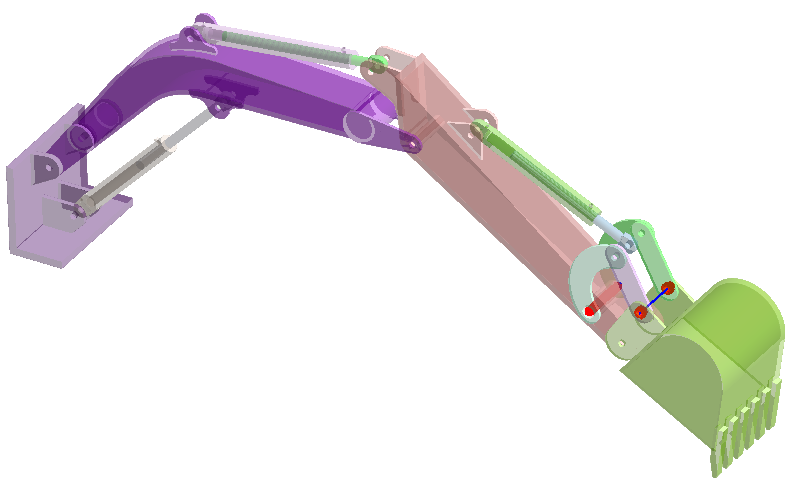
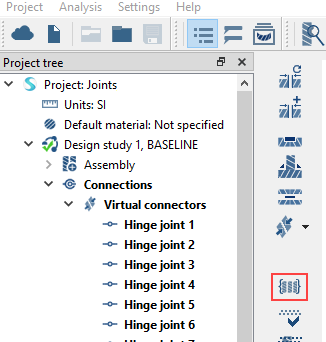
Review Connections
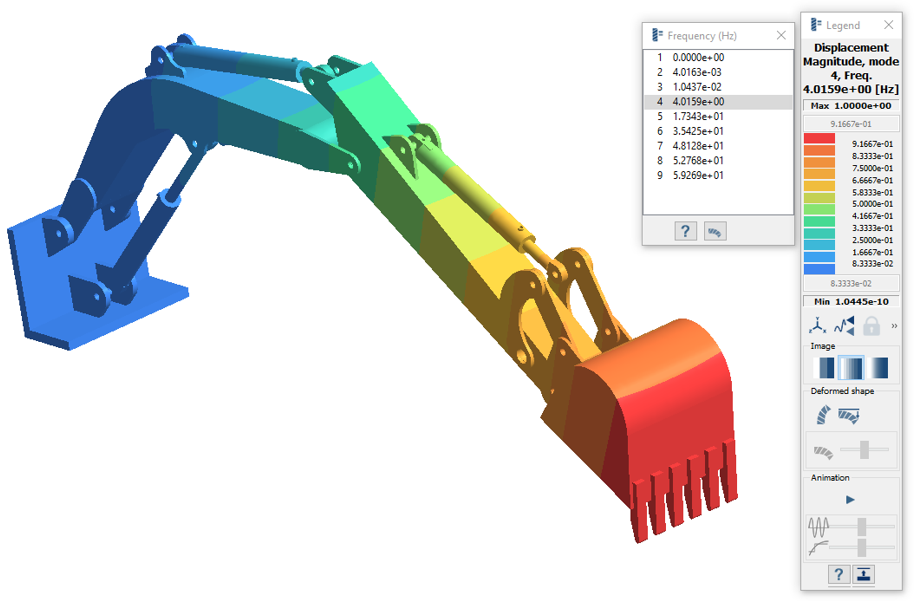
Run Analysis
- On the Project Tree, open the Analysis Workbench.
-
Click
 (Solve).
(Solve).