Domain
In the domain section, the global definitions for the simulation are set, such as the number of dimensions and the numerical reference parameters.
Commands
domain
{
ndim 3
min_domain "0.0 0.0 0.0"
max_domain "1.0 3.0 0.0"
BC_min "OUTLET PERIODIC SIMPLEOUTLET"
BC_max "OUTLET PERIODIC SIMPLEOUTLET"
outlet_vel "0.05 0.0 0.0"
outlet_bodyforce_on true
ref_rho 1000.
ref_length 0.1
ref_vel 1.0
ref_curv 1.0
ref_visc 1.0
bodyforce "0. 0. 0."
t_damp_bodyforce_start 0.
t_damp_bodyforce_end 0.
bodyforcefile inputFileName.txt
inputfile initialparticlepositions.txt
inputfileReadMode AUTO
inputfile_factor 0.001
}Definitions
| Command | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| ndim | The dimensionality of the problem. 1 Options
|
|
| min_domain | Minimum bounds of the computational box (vector defining a point
location). Note: If both min_domain and
max_domain are not specified in the
configuration file, the variables will be determined by the code
automatically. 1
|
|
| max_domain | Maximum bounds of the computational box (vector defining a point
location). Note: If both min_domain and
max_domain are not specified in the
configuration file, the variables will be determined by the code
automatically. 1
|
|
| BC_min | Boundary condition at the minimum boundary. For an illustration
of domain boundaries, refer to Comment 2. Options
Related Commands
|
|
| BC_max | Boundary condition at the maximum boundary. For an illustration
of domain boundaries, refer to Comment 2. Options
Related Commands
|
|
| outlet_vel | Specifies the velocity of the OUTLET boundary. Note:
|
|
| outlet_bodyforce_on | If this flag is switched on, the outlet particles will experience
the prescribed body force. This is useful in cases where the outlet
plane is perpendicular to the body force (gravity) direction. In
these case, the zero gradient velocity at the outlet no longer applies. Options
|
|
| ref_rho | Reference density. This should be the lowest fluid density in the
domain. Important: All reference values have been automated. They can be set
manually, as is recommended. Depending on the case definition,
the code will automatically pick up the reference values,
provided that the max_dist command is defined
in the motion definition.
Note: For density, the lowest
fluid density is picked up as the reference.
Default = If not specified, the code will automatically detect it. |
|
| ref_length | Reference length. A typical length scale defining the relevant
physics. Note: It is recommended that you specify this reference
value, as it can be difficult for the code to identify the
correct value in certain cases. For length, the code will
analyze the size of the domain in the direction of the body
force applied and choose that length as the reference length.
This means that if variable body force is being used, the
reference length is specified manually. Examples:
Default = The code will automatically try to find a relevant length for a hydrostatic problem. |
|
| ref_vel | Reference velocity. Should be the highest expected velocity in
the domain. Note: For velocity, if there is defined motion in the
configuration file, the code will automatically calculate
maximal velocity of the motion, multiply it by a
ref_vel_factor (the default value is 1.5)
for conservative purposes, and set that value as the reference
velocity. If there is no motion defined, or if the motion is
rigid body or position file, the reference velocity must be
defined manually.
Default = If the motion is defined in the .cfg file, the code will automatically calculate the maximum velocity and multiply it by the ref_vel_factor value in order to assure stable running of the simulation. |
|
| ref_curv | Reference curvature (needed only if
surften_model is set to
ADAMI or SINGLE_PHASE). Should
be the curvature of the smallest droplet that needs to be resolved
(1/radius of the droplet). Note: For reference curvature, the default
curvature is set as 1/(5*dx). In order to
resolve droplets accurately, there needs to be a droplet radius
of at least five particles.
Default = If not specified, the value is set to 1/(5*dx) Related Commands
|
|
| ref_visc | Reference viscosity (needed only if
viscTempCoupling is set to true). Should be
the highest expected viscosity in the domain. Related Commands
|
|
| bodyforce | Gravitational acceleration. Note: Body force vector must be
specified (if using variable body force file, the latter
bodyforcefile command will overwrite
it).
|
|
| t_damp_bodyforce_start | Before this time, the
body force is zero. Starting from this time, a gravitational
acceleration is added to the system. Note: Ramping up to the given
value is defined with t_damp_bodyforce_start
and t_damp_bodyforce_end
commands.
Default = 0 |
|
| t_damp_bodyforce_end | This time must not be
smaller than t_damp_bodyforce_start. Within the
time interval between t_damp_bodyforce_start and
t_damp_bodyforce_end the gravitational
acceleration is ramped up to reach the full body force at
t_damp_bodyforce_end. At later times the full
body force is applied. Default = 0 |
|
| bodyforcefile | Name of the file that contains the body force vector as a
function of time, allowing simulations of sloshing tanks. This is
simultaneously a switch for the code. If you have this command
present, it will use the specified input file and ignore the
previous bodyforce input. Related Commands
|
|
| inputfile | This file is the geometry input file (textfile) and needs to be present in the folder where the simulation is launched together with the config-file. | |
| inputfile_factor | This factor can be used to scale the input file
content. Note: nanoFluidX uses SI-units.
Therefore, this factor is useful if a model is created in
SimLab in millimeter-units and
needs to be converted to meters while reading in. Example:
Default = 1.0 |
|
| inputfileReadMode | Describes the data format that is to be read in. Options
|
Comments
- If both min_domain and max_domain are not specified in the configuration file, the code will automatically detect the minimum and maximum dimensions of the case and create a bounding box automatically. This is useful when operating with closed geometry, such as a gearbox. To simulate a sloshing/splashing case where the fluid is not constrained within solid walls, or if there are periodic or inlet boundary conditions associated with the domain, it is necessary to manually prescribe the size of the domain (bounding box). [ndim, min_domain, max_domain]
- Each of the six bounding planes is
marked in a separate color, with the colored arrow showing the surface
normal of the boundary. The direction of these surface normals in the sketch
has no influence on the code execution, they are provided to help visualize
the domain. The two red dots at the opposite corners of the domain are
minimum and maximum extent of the domain. [BC_min, BC_max]
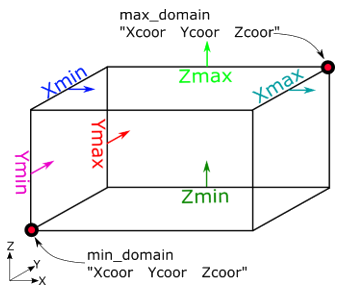
Figure 1. Sketch of nanoFluidX domain boundaries