Specify Fans
Identify the components that represent fans in the model.
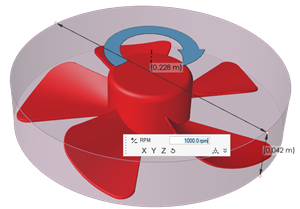
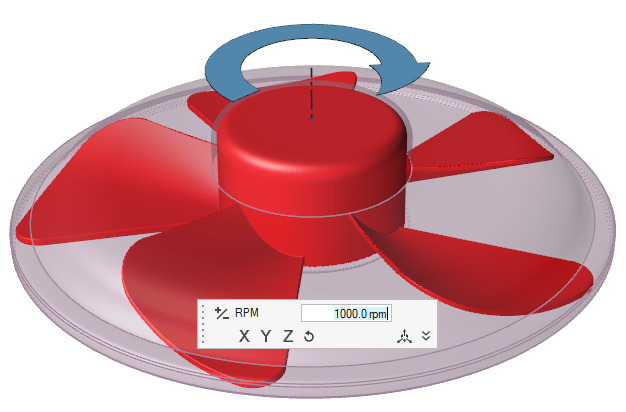
Fans are modeled like wheels, a boundary condition is prescribed and a rotational speed is applied.
You select the parts that form the fan, such as blades and hub. The center and axis of rotation are automatically computed. However, the rotational speed needs to be provided.
Aerodynamics and aeroacoustics supports three model approaches for fans:
- Frozen
- The fan does not rotate in the simulation.
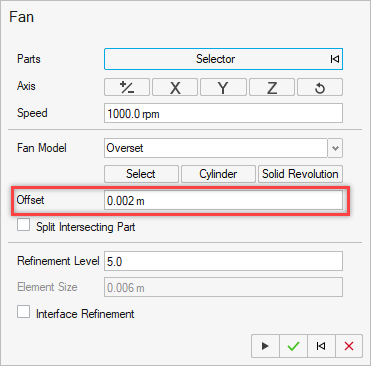
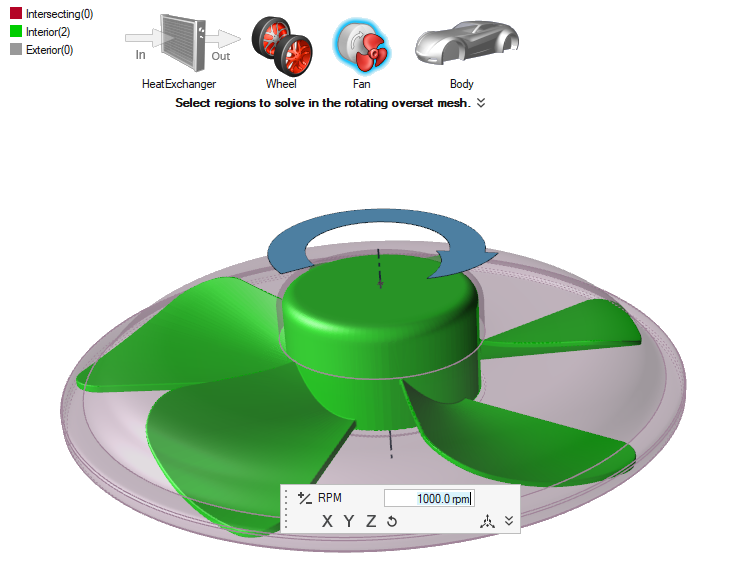
- Overset
- The fan and mesh inside is rotated to accurately represent the flow and rotating fan.
- MRF
- The fan does not rotate in the simulation. An MRF volume improves the modeling of the swirling flow created by a fan.
- Virtual
- Applies a body force to a volume to mimic a fan.