FE Geometry
FE geometry is topology on top of mesh, meaning CAD and mesh exist as a single entity. The purpose of FE geometry is to add vertices, edges, surfaces, and solids on FE models which have no CAD geometry.
Tools and workflows operate similarly on CAD as they do with FE. With FE geometry, mesh selections are made easier as they are topology-based.
FE geometry can be used for 1D and 2D elements. It is recommended to use FE geometry where there is no associated CAD.
FE Geometry Creation
FE geometry creation in HyperMesh tools is controlled from .
When the create mode is set to CAD geometry, all points, lines, surfaces, and solids created will be CAD geometry.
When the create mode is set to FE geometry, all points, lines, surfaces, and solids created will be FE geometry.
Midmesh default extraction output will be FE geometry only.
Creation Rules Applied in Tools and Workflows
- For CAD geometry inputs, expected output is CAD geometry.Ruled surface creation from two CAD edges gives CAD geometry surface.
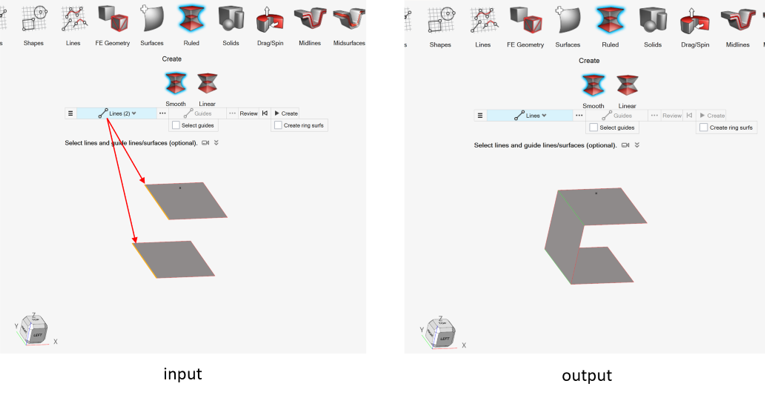
Figure 1. - For FE geometry inputs, expected output is FE geometry.Ruled surface creation from two FE geometry edges gives FE geometry surface.
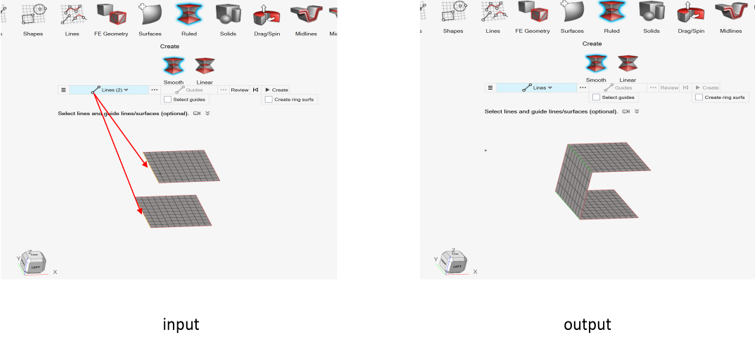
Figure 2. - For mixed inputs (CAD geometry + Fe geometry), expected output is CAD
geometry.Ruled surface creation from mixed selection (CAD edge and FE geometry edge), gives CAD surface.
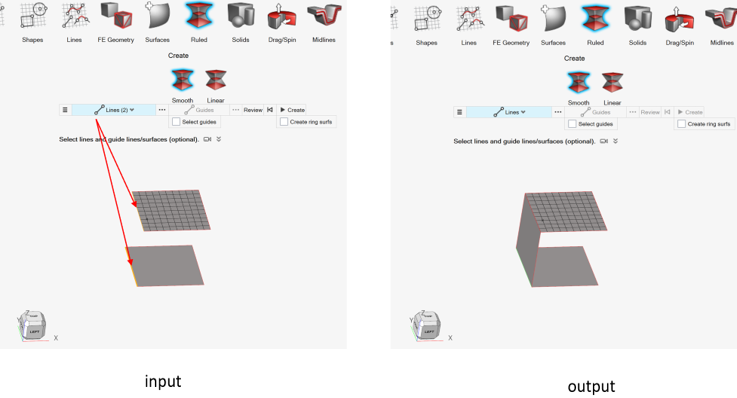
Figure 3.
FE Topology Revision
FE topology revision in HyperMesh tools is controlled from .
Any of the three methods can be used for FE topology revision.
- Keep mesh
- Keep existing mesh on FE topology revision.
- Remesh
- Remesh surrounding mesh on FE topology revision.
- Rebuild
- Rebuild surrounding mesh on FE topology revision.
- Number of layers
- Define the zone to be remeshed or rebuild on topology revision.
Convert To and Update FE Geometry
Use the FE Geometry tools to convert elements or CAD surfaces into FE geometry, or update existing FE geometry.
FE Geometry Visualization
- Organizing an FE geometry surface to a new component will move all its
surface elements to that component.
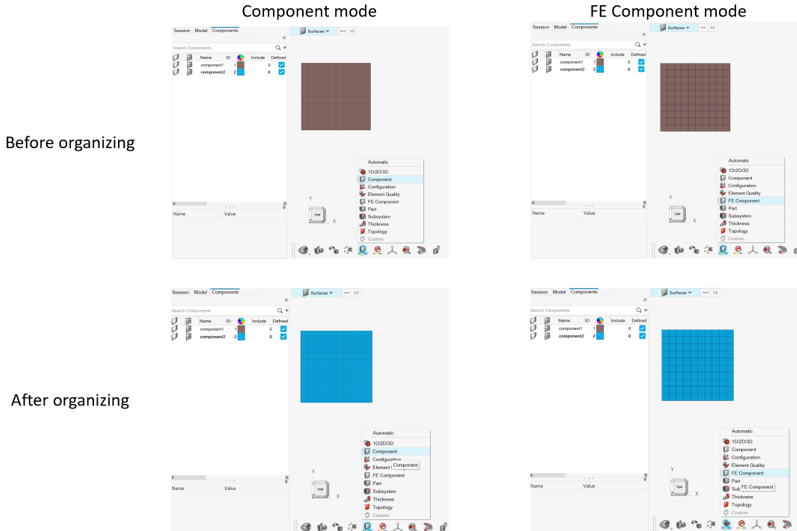
Figure 6.Note: The surface and its elements belong to the same component.As a recommendation, it is suggested to keep FE geometry surfaces and their elements in the same component. However, in some cases like map thickness, elements can be organized in different components.
Functionalities Without FE Geometry Support
Below is a list of functionalities not yet supporting FE geometry in HyperMesh 2023
Geometry
- Extend: Stitch at target using “Auto trim intersecting surface” option is not supported.
- Cross Extend
- Offset
- Drag/Spin: Preview of FE geometry solid is not available.
- Midlines: FE geometry solid is not supported
- Midsurfaces
- Split > Lines: FE geometry line split is not supported.
- Split > Surfaces: Extend trimmer is not supported for FE geometry.
- Split > Surfaces: “Trim both” is not supported for mixed selection.
- Split > Surfaces: “Self-intersecting surfaces” is not supported for mixed selection.
- Split > Surfaces: Split CAD using FE geometry is not supported.
- Split > Plane: FE geometry line split is not supported.
- Split > Plane: Review is not available for FE geometry solid split.
- Stitch: Mixed selection is not supported.
- Suppress: Mixed selection is not supported.
- Unsuppress
- Fillets
- Boolean
- Plug
- Defeature > Cuts, Small Features, Logos, Fillets and Batch
- Preserve Edges
Mesh
- Batchmesh and Rigid body meshing does not support FE geometry as input.
- Assign plot contour is not supported for FE geometry elements in the Check elements (F10) 1D & 2D panel.
- Tetra: FE geometry solid elements creation is not supported.
- Hex: FE geometry solid elements creation is not supported.
- Solid Map: FE geometry solid elements creation is not supported
- Thin Solids: FE geometry solid elements creation is not supported.
Elements
- Refine > Auto quads and Box
- Imprint/Extend
- Normals: Display and adjust normals for FE geometry surface is not supported.