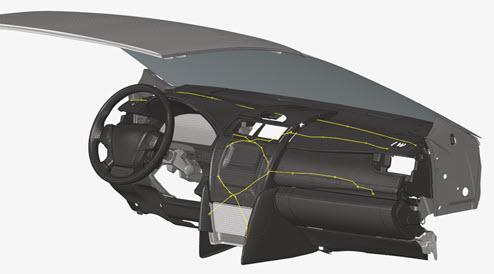
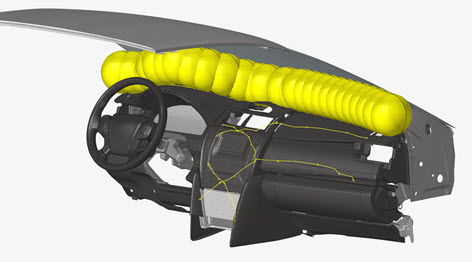
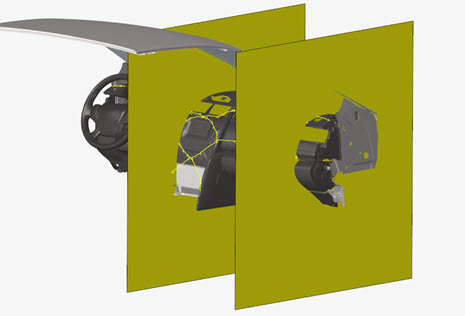
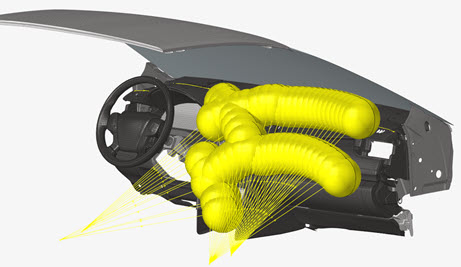
IP Impact
Use the IP Impact tools to automatically calculate the instrument panel (IP) testing area according to the regulations FMVSS201 and ECE-R21, position the headform impactor, and export ready-to-run solver decks for all the selected impact locations.
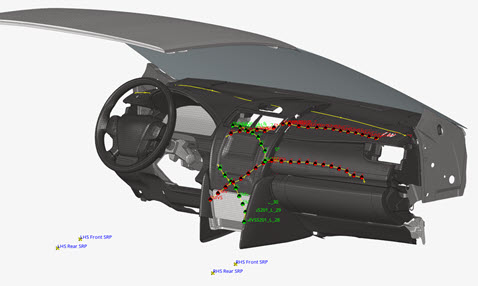
Figure 1.
IP Marking
 after each selector to reset your selection. Click
after each selector to reset your selection. Click
 at the end of the guide bar to
delete all marking entities previously created.
at the end of the guide bar to
delete all marking entities previously created.Automatic Marking
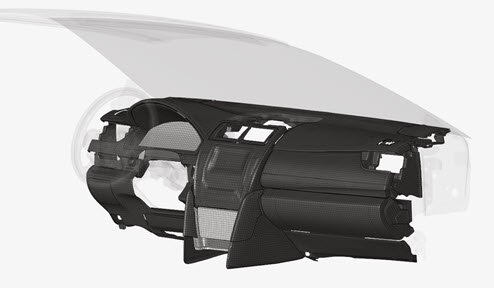
Figure 2. Instrumental Panel components
Steering wheel and Windshield can be selected for the calculation of the limits of the impact area as defined in the regulation.
At the end of the marking workflow, the following entities are generated:
- Geometrical lines
- Defining the upper and lower limits of the impact area.
- Sphere surfaces
- Defining the construction of the upper limit for the FMVSS201 regulation.
- Planes
- Defining the right and left limits of the impact area as per the regulations.
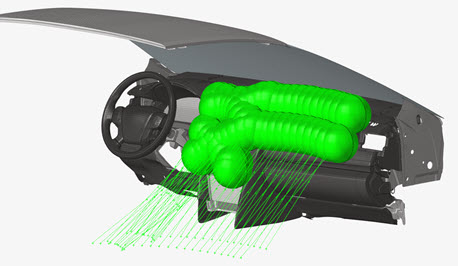
- Impactor geometries
- Defining the position of the impactor used for the impact area lines generation.
- Design Points entities
- Defining entities at the calculated impact locations.
- Impactor geometries
- Defining the pre-calculated impactor position with the given Arm Length.

Figure 9.
Manual Marking
Manual marking allows you to create a Design Point entity at a selected location on the IP. A minimum of Design Point entity metadata can be specified in the options menu.
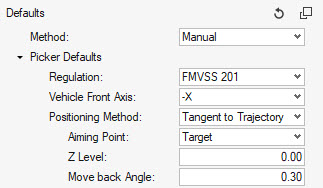
Figure 10.
Select the impact location from the guide bar. Click Mark to automatically generate the Design Point entities.

Figure 11.
Test Lab Marking
Test Lab marking allows you to directly read a CVS file containing the information for the impact locations that a test laboratory can provide.
Select the CSV file from the options menu options then click Mark to automatically create the Design Point entities at the defined locations.
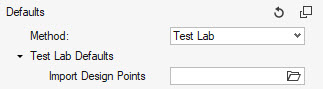
Figure 12.
Here is an example of a CSV file:
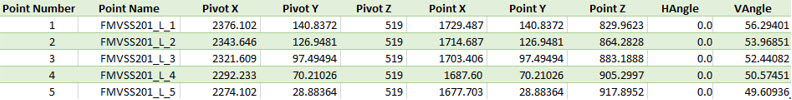
Figure 13.
IP Positioning
After the creation of Design Points from the Marking process, the Positioning workflow is used to:
- Calculate the position of the impactor for all the selected Design Points.
- Visualize the position of the impactor.
- Export ready-to-run solver decks for all the selected Design Points
 after each selector to reset your selection. Click
after each selector to reset your selection. Click
 at the end of the guide bar to
reset all calculated impactor positions.
at the end of the guide bar to
reset all calculated impactor positions.Pre-Requisites on the Headform Model
This tool can position pendulum headform and linear headform (Normal to Target positioning).
In both cases, a coordinate system at the center of the headform with the X axis pointing in the travel direction needs to be defined.
The velocity should be defined in the impactor model since this tool doesn’t generate it automatically.
Positioning Methods
Tangent to Trajectory
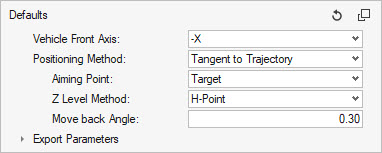
Figure 14.
Selecting this method positions the headform with the target location on the circular trajectory of the center of the head.
The Aiming Point can be either Target or Contact point.
The Z Level Method fixes the Z coordinate of the pivot of the headform. Per default, it is set to the H-Point Z coordinate (= Seat Reference Point Z coordinate in the Design Point metadata). It can be switched to User defined, and you can provide a value.
The Move back Angle is applied once the impactor position is calculated in order to avoid intersections with the instrumental panel.
The metadata defined in the selected Design Point entity is ignored and overwritten with the values calculated by this positioning method.
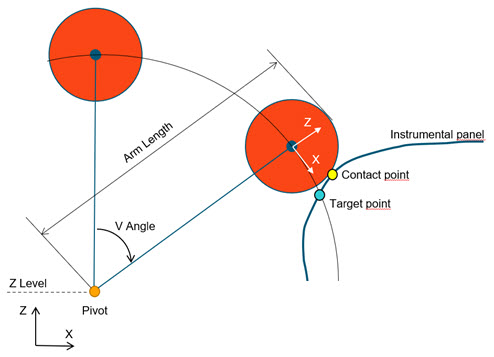
Figure 15. Tangent to Trajectory positioning
Normal to Trajectory
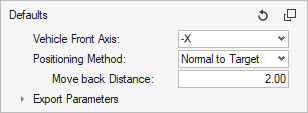
Figure 16.
Selecting this method positions the headform with the IP-normal at target location aligned on the X-Axis of the coordinate system at the center of the headform.
The IP-normal vector is determined with the surrounding elements at the target location.
A pivot node selection is not requested.
The Move back Distance is applied once the impactor position is calculated in order to avoid intersections with the instrumental panel.
The metadata defined in the selected Design Point entity is ignored and overwritten with the values calculated by this positioning method.
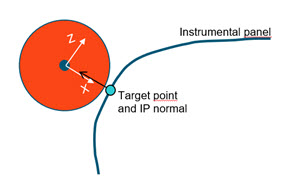
Figure 17. Normal to Trajectory positioning
Pivot/Angles
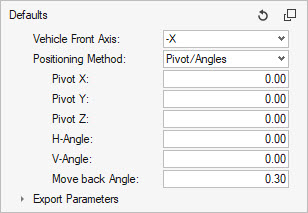
Figure 18.
Selecting this method positions the headform by moving the pendulum pivot to the given (Pivot X, Pivot Y, Pivot Z) location, and applying successively the V-Angle around the global Y axis and H-Angle around the transformed X-Axis. (X’)
The Move back Angle is applied once the impactor position is calculated in order to avoid intersections with the instrumental panel.
Since pivot and angles are directly given as input, the target point may not necessarily be on the trajectory of the headform.
The metadata defined in the selected Design Point entity is ignored and overwritten.
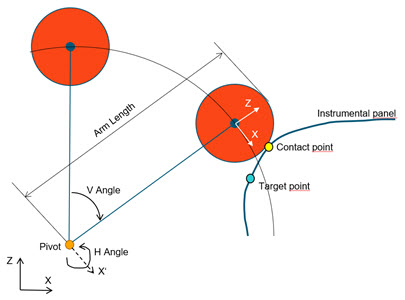
Figure 19. Pivot/Angles positioning
Target/Angles
Figure 20.
Selecting this method positions the headform by applying the H and V angles around the Target point location.
The pivot location is not an input and results from the application of both angles.
The Move back Distance is applied once the impactor position is calculated in order to avoid intersections with the instrumental panel.
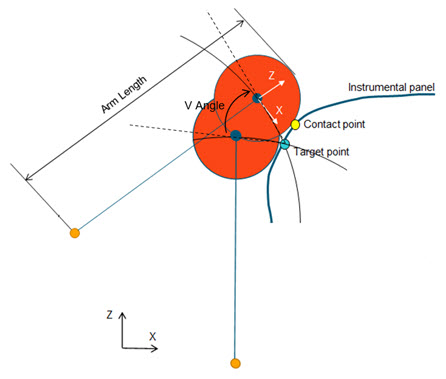
Figure 21.
Automatic
Figure 22.
Selecting this method positions the headform according to the positioning parameters defined in the Design Point entity.
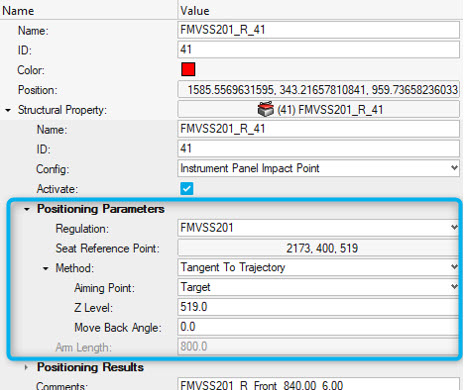
Figure 23.
Export Solver Decks
This tool enables you to export ready-to-run solver decks for all the impact locations.
In the IP Positioning Workflow, provide the information in the Export Parameters.
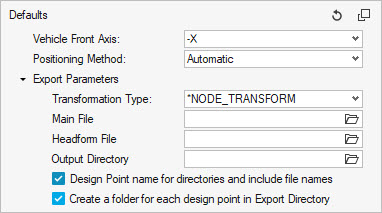
Figure 24.
The Main File is the user-defined main input deck containing the include structure of the final model (IP model, contacts, controls, boundary conditions, …)
Here is an example of a Main File for LS-DYNA:
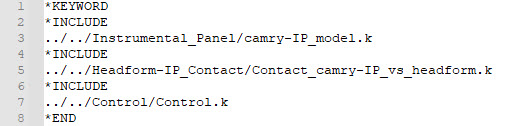
Figure 25.
And here is an example for Radioss:
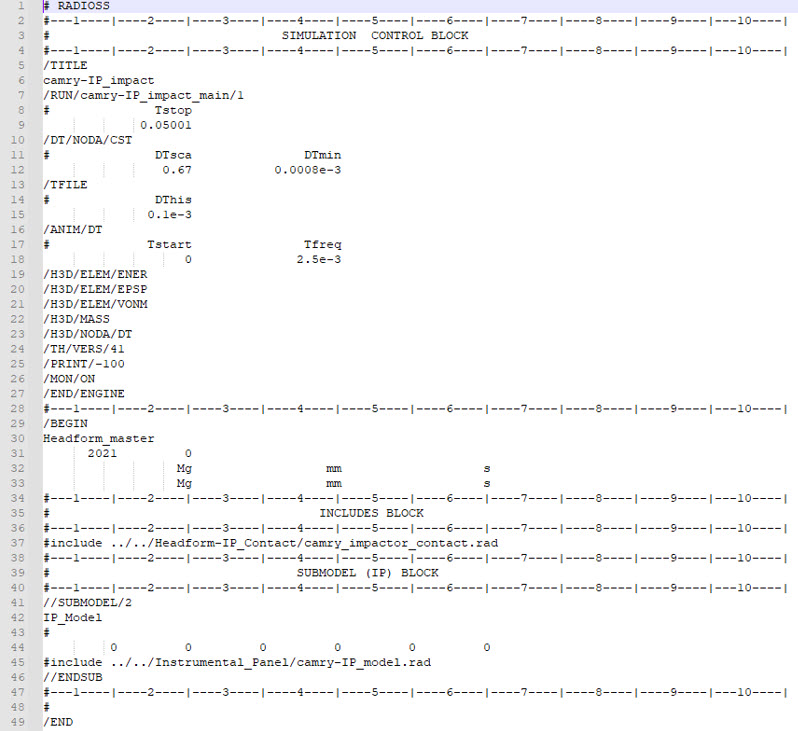
Figure 26.
Headform File should point to the headform model that the tool will define as an include in the Main File during the export of the decks.
The Output Directory is the location where all the solver decks for each impact location are written out.
During the export process, the tool generates an additional include file containing the transformations to apply on the impactor using the Transformation Type.
Example of positioning include file generated by the tool:
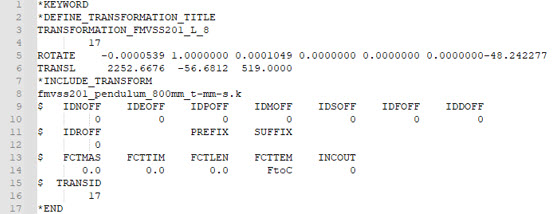
Figure 27. LS-DYNA
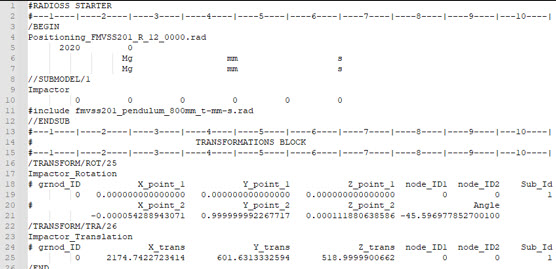
Figure 28. Radioss
Finally, the positioning file is automatically added as an include file in the Main File. The resulting model files for each impact location look as follows:
- FMVSS201_L_8.k
- fmvss201_pendulum_800mm_t-mm-s.k
- Positioning_FMVSS201_L_8.key
- fmvss201_pendulum_800mm_t-mm-s.rad
- FMVSS201_R_12_0000.rad
- Positioning_FMVSS201_R_12_0000.rad
 and
and  to
cycle through the entity types for the marking process.
to
cycle through the entity types for the marking process.