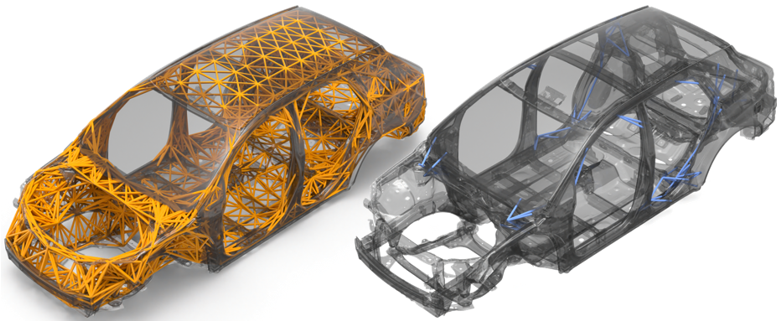
Exoskeleton
Promotes design exploration of early concepts and mature structures.
The Exoskeleton tool provides insight as to how the structure may need reinforcing to meet a predetermined performance criteria.
- Topology
- Provides high-level design direction to determine where the structure can benefit from reinforcing.
- Size
- If the location is known or the design space location is defined already, use Size optimization to provide design direction more accurately, as it provides accurate diameter and wall thickness as a result.
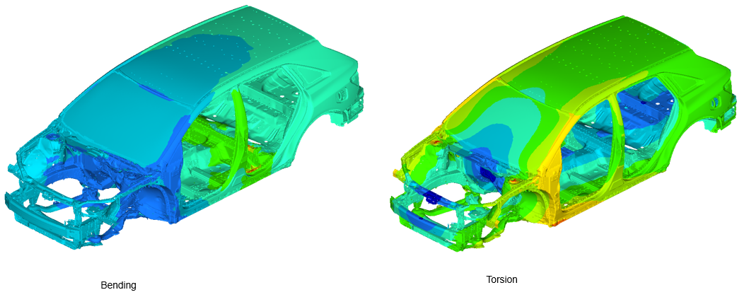
Figure 2.
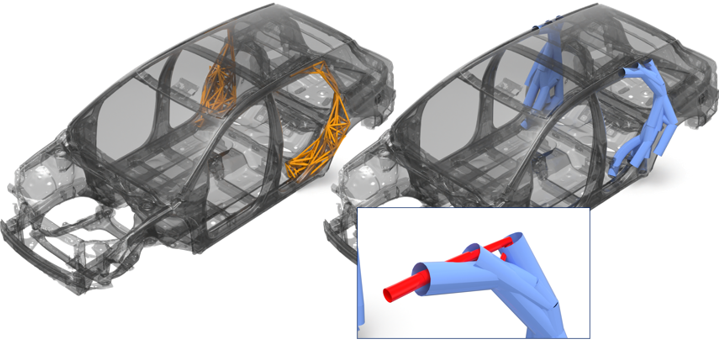
- Topology Optimization
- In the figure below, the image on the left illustrates the newly generated exoskeleton (see orange 1D elements). These 1D elements define the exoskeleton lattice design space. The exoskeleton has tied contact defined between the nodal junctions of the exoskeleton (secondary set) and the original structure (main set). One single DTPL design variable is automatically created.
- Size Optimization
- In this example, the location of the design space is known (see the orange 1Ds), however the reinforcement composition details are unknown. The figure on the right (the blue elements) is the result of the size optimization. All beam elements that have little or no influence are manually deleted. The remaining elements provide the necessary design guidance. In this case, it retains the 1Ds that give the largest footprint in that localized area and maximizes the diameter while minimizing the wall thickness (to reduce mass). Results vary depending on the optimization problem definition.