Load Export
An external module invoked from MotionView. This module allows you to take loads from an ADAMS run and create a tabular summary file or a Nastran input card for those loads.
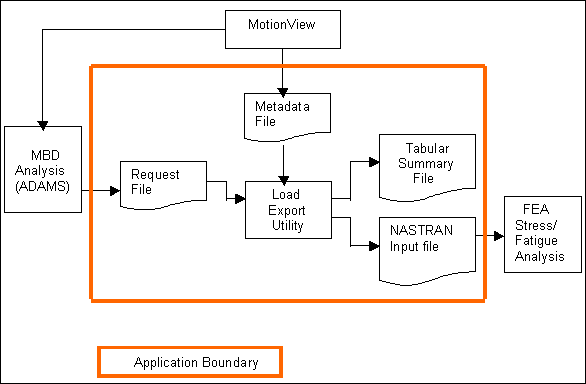
Figure 1. Interaction diagram
Metadata File Generation and Format
MotionView supports force requests on body entities. To provide detailed information about the forces acting on a given body entity, MotionView automatically generates a metadata file if there are active force requests on body entities in the active model. For more information, see the Metadata File Generation and Metadata File Format topics.
To run the Load Export utility:
- The Load Export utility is displayed.