Fatigue using E-N (Strain - Life) Method
The E-N (Strain - Life) method should be chosen to predict the fatigue life when plastic strain occurs under the given cyclic loading. S-N (Stress - Life) method is not suitable for low-cycle fatigue where plastic strain plays a central role for fatigue behavior.
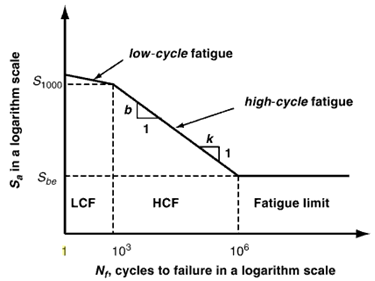
Figure 1. Low Cycle and High Cycle Regions on the S-N Curve
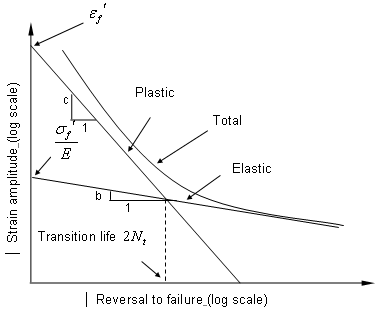
Figure 2. Strain-Life Curve
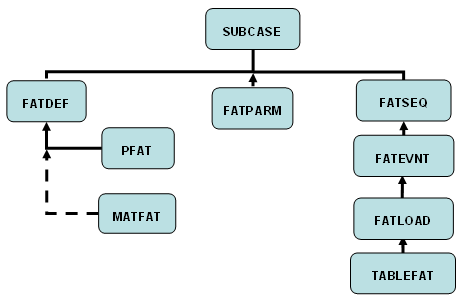
Figure 3. Fatigue Analysis Flowchart
- FATDEF
- Defines the elements and associated fatigue properties that will be used for the fatigue analysis.
- PFAT
- Defines the finish, treatment, layer and the fatigue strength reduction factors for the elements.
- MATFAT
- Defines the material properties for the fatigue analysis. These properties should be obtained from the material's E-N curve (Figure 2). The E-N curve, typically, is obtained from completely reversed bending on mirror polished specimen.
- Fatigue Parameters
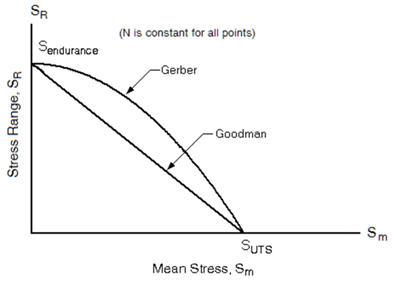
Figure 4. Mean Stress Correction- FATPARM
- Defines the parameters for the fatigue analysis. These include stress combination method, mean stress correction method (Figure 4), Rainflow parameters, and Stress Units.
- Fatigue Sequence and Event Definition
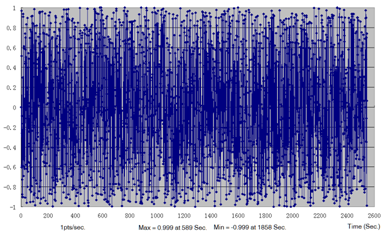
Figure 5. Load Time History- FATSEQ
- Defines the loading sequence for the fatigue analysis. This card can refer to another FATSEQ card or a FATEVNT card.
- FATEVNT
- Defines loading events for the fatigue analysis.
- FATLOAD
- Defines fatigue loading parameters.
- TABLEFAT
- Defines the y values for each point on the time loading history (Figure 5).
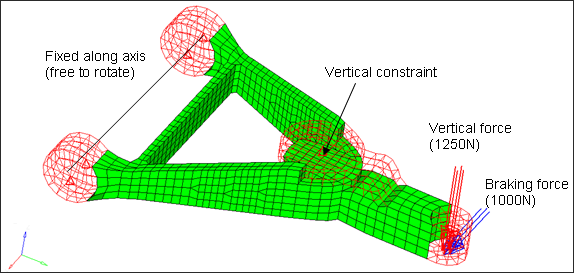
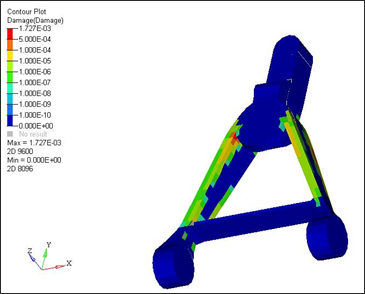
Figure 6. Model of the Control Arm for Fatigue Analysis
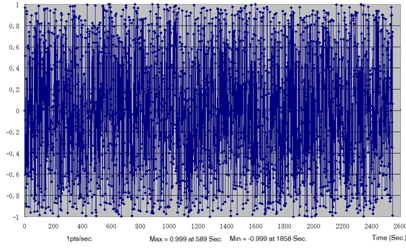
Figure 7. Load Time History for Vertical Force
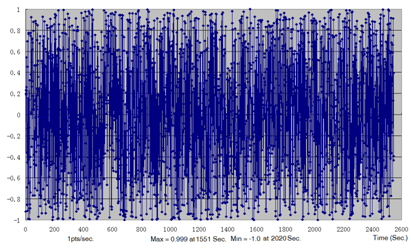
Figure 8. Load Time History for Braking Force
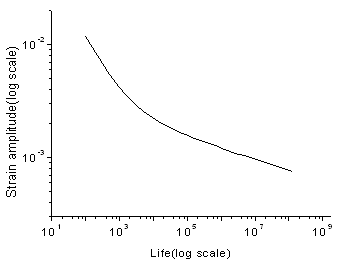
Figure 9. EN Curve of Aluminum
The model being used for this exercise is that of a control arm as shown in Figure 1. Loads and boundary conditions and two static loadcases have already been defined on this model.
Launch HyperMesh and Set the OptiStruct User Profile
Import the Model
Set Up the Model
Define TABFAT Load Collector
Define FATLOAD Load Collector
- In the Model Browser, right-click and select .
- For Name, enter FATLOAD1.
- Click Color and select a color from the color palette.
- For Card Image, select FATLOAD.
- For TID(table ID), select table1 from the list of curves.
- For LCID (load case ID), select SUBCASE1 from the list of load steps.
- Set LDM (load magnitude) to 1.
- Set Scale to 5.0.
- Repeat the process to create another load collector named FATLOAD2 with FATLOAD Card Image and pointing to table2 and SUBCASE2.
- Set LDM to 1 and Scale to 5.0.
Define TABEVNT Load Collector
- In the Model Browser, right-click and select .
- For Name, enter FATEVENT.
- For Card Image, select FATEVNT.
- Set FATEVNT_NUM_FLOAD to 2.
-
Click on the Table icon
 next to the
Data field and select FATLOAD1 for
FLOAD(1) and FATLOAD2 for FLOAD(2) in
the pop-out window.
next to the
Data field and select FATLOAD1 for
FLOAD(1) and FATLOAD2 for FLOAD(2) in
the pop-out window.
Define TABSEQ Load Collector
Define Fatigue Parameters
- In the Model Browser, right-click and select .
- For Name, enter fatparam.
- For Card Image, select FATPARM.
- Verify TYPE is set to EN.
- Set STRESS COMBINE to SGVON (Signed von Mises).
- Set STRESS CORRECTION to SWT.
- Set STRESSU to MPA (Stress Units).
- Set PLASTI to NEUBER (plasticity correction).
- Set RAINFLOW RTYPE to STRESS.
Define the Fatigue Material Properties
The material curve for the fatigue analysis can be defined on the MAT1 card.
Define PFAT Load Collector
- In the Model Browser, right-click and select .
- For Name, enter pfat.
- For Card Image, select PFAT.
- Set LAYER to TOP.
- Set FINISH to NONE.
- Set TRTMENT to NONE.
Define FATDEF Load Collector
- In the Model Browser, right-click and select .
- For Name, enter fatdef.
- Set the Card Image to FATDEF.
- Activate PTYPE and PSHELL in the PTYPE Entity Editor.
- Click the PID, PFATID option to open the dialog.
- For PID, select shell.
- For PFATID, select pfat.
- Click Close.
Define the Fatigue Load Case
- In the Model Browser, click on
- For Name, enter Fatigue.
- Set the Analysis type to Fatigue.
- For FATDEF, select fatdef.
- For FATPARM, select fatparam.
- For FATSEQ, select FATSEQ.
 .
. 
 to open the
to open the